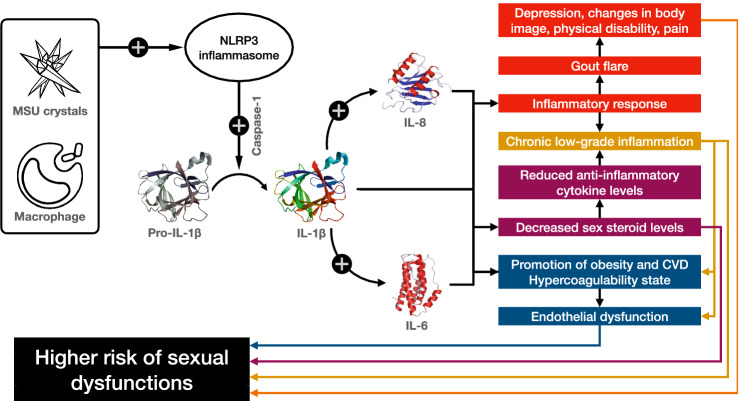
Fig. 2.
The pathogenetic mechanisms linking gout and sexual dysfunctions. The activation of the NOD-, LRR-, and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome occurring upon interaction between macrophages and monosodium urate (MSU) crystals results in increased levels of caspase-1, which transforms pro-interleukin-1β (pro-IL-1β) to the bioactive IL-1β, the main driver of inflammation in gout. The subsequent inflammatory cascade, which also involves IL-6 and IL-8, affects sexual function by several direct and indirect pathways. CVD: cardiovascular diseases