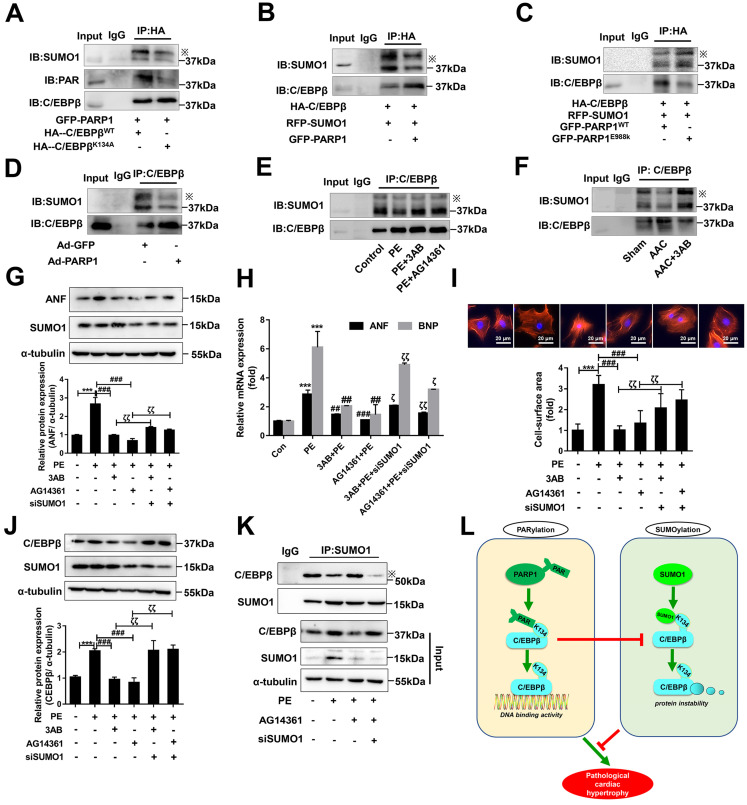
Figure 7.
The cross-talk between C/EBPβ K134 SUMOylation and PARylation participates in PARP1-induced cardiac hypertrophy. (A) NRCMs were transfected with the expression vectors for GFP-PARP1, HA-C/EBPβWT and HA-C/EBPβK134A as indicated, immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody and followed by Western blot with anti-PAR, anti-SUMO1 or anti-C/EBPβ antibody. ※ indicates C/EBPβ-SUMO. n=3. (B, C) HA-C/EBPβ, RFP-SUMO1, GFP-PARP1WT and GFP-PARP1E988K were expressed in NRCMs as indicated. immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody and followed by Western blot with anti-SUMO1 or anti-C/EBPβ antibody. ※ indicates C/EBPβ-SUMO. n=3. (D) SD rats were submitted to intracardiac injection of adenovirus encoding PARP1 (Ad-PARP1, 1010 particles), the control animals received green fluorescent protein (Ad-GFP, 1010 particles). The rat heart tissue was immunoprecipitated with anti-C/EBPβ antibody and subsequently subjected to Western blot with anti-SUMO1 or anti-C/EBPβ antibody. ※ indicates C/EBPβ-SUMO. n=3. (E) NRCMs were treated with 3-aminobenzamide (3AB) (20 μmol/L) or AG14361 (1 μmol/L), followed by incubation with PE (100 μmol/L for 24 h), immunoprecipitated with anti-C/EBPβ antibody and subsequently subjected to Western blot with anti-SUMO1 or anti-C/EBPβ antibody. ※ indicates C/EBPβ-SUMO. n=3. (F) PARP1 inhibitor 3AB was intraperitoneally injected (20 mg/kg, twice daily) starting the week after AAC surgery for 7 weeks, the heart tissues were immunoprecipitated with anti-C/EBPβ antibody and subsequently subjected to Western blot with anti-SUMO1 or anti-C/EBPβ antibody. ※ indicates C/EBPβ-SUMO. n=3. (G) NRCMs were transfected with siSUMO1 or incubated with 3AB (20 μmol/L) or AG14361 (1 μmol/L) followed by incubation with PE (100 μmol/L for 24 h). The protein level of ANF was determined by western blot. ***P < 0.001 vs. Con group, ###P < 0.001 vs. PE group, ζζP < 0.01 vs. PE+3AB or PE+AG14361 group, (n=3). (H) The mRNA levels of ANF and BNP were determined by qRT-PCR. ***P < 0.001 vs. Con group, ##P< 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. PE group, ζP < 0.05, ζζP < 0.01 vs. PE+3AB or PE+AG14361 group, (n=3). (I) Cell surface area was measured by rhodamine staining. ***P < 0.001 vs. Con group, ###P < 0.001 vs. PE group, ζζP < 0.01 vs. PE+3AB or PE+AG14361 group, (n=3). (J) The protein level of C/EBPβ was determined by western blot. ***P < 0.001 vs. Con group, ###P < 0.001 vs. PE group, ζζP < 0.01 vs. PE+3AB or PE+AG14361 group, (n=3). (K) NRCMs were transfected with siSUMO1 or incubated with AG14361 (1 μmol/L) followed by incubation with PE (100 μmol/L for 24 h), immunoprecipitated with anti-SUMO1 antibody and subsequently subjected to Western blot with anti-SUMO1 or anti-C/EBPβ antibody. n=3. (L) Schematic model to show the posttranslational modifications of C/EBPβ and the roles they may play in pathological cardiac hypertrophy. PARP1 directly interacts with C/EBPβ and induce PARylation of C/EBPβ at K134 site in a conserved domain. The accumulation of PARylation of C/EBPβ at K134 site exhibits downregulation of C/EBPβ SUMOylation at the same site and results in upregulation of C/EBPβ protein stability. SUMO1 participates in PARP1-induced cardiac hypertrophy, which depends on SUMOylation at K134 site and protein level of C/EBPβ.