Fig 2. Critical alternative splicing events during EMT.
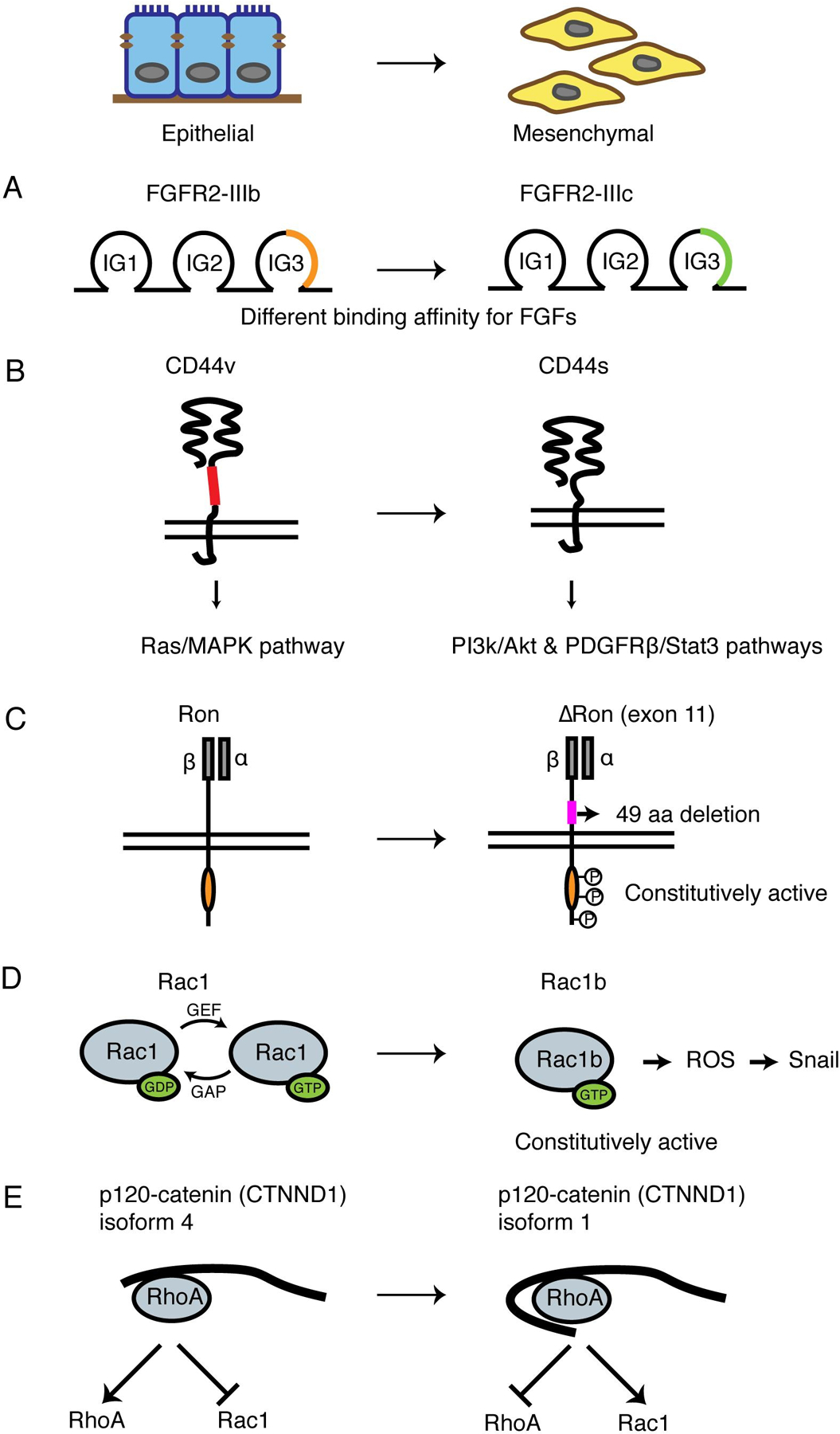
(A) Schematic of FGFR2 alternative splicing during EMT. Isoform switching from the epithelial FGFR2-IIIb to the mesenchymal FGFR2-IIIc changes the structure of an immuoglobin-like domain to enhance the binding affinity to FGF.
(B) Schematic of CD44 alternative splicing during EMT. Epithelial isoform CD44v has a longer extracellular stem region than mesenchymal isoform CD44s. The two isoforms activate Ras/MAPK pathway and PI3K/Akt, PDGFRβ/Stat3 pathways, respectively.
(C) Schematic of Ron alternative splicing during EMT. The mesenchymal isoform ∆Ron lacks a 49-amino acid region in the extracellular domain of the β-subunit and is constitutively active.
(D) Schematic of Rac1 alternative splicing during EMT. The mesenchymal Rac1b isoform is in the GTP-bound active conformation, generating ROS and induces SNAI1 expression.
(E) Schematic of p120-catenin (CTNND1) splicing during EMT. Mesenchymal isoform 1 is the longest isoform that contains a coiled-coil domain and a regulatory domain, inhibiting RhoA activity and promoting Rac1 activity. The epithelial isoform 4 lacks both domains and promotes RhoA activity.
