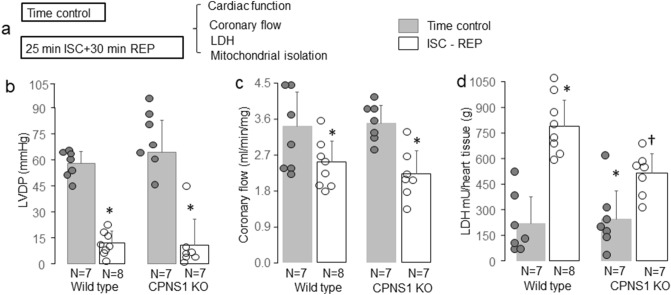
Figure 2.
Elimination of CPNS1 decreases cardiac injury during ISC–REP. WT or CPNS1 deletion mouse hearts underwent 25 min global ischemia and 30 min reperfusion. Mouse hearts in time control groups underwent buffer perfusion without ischemia (a). ISC–REP led to decreased left ventricular developed pressure (LVDP) in both WT and deletion mice compared to time control (b). ISC–REP led to decreased coronary flow in both WT and deletion mice compared to time control (c). ISC–REP also increased the release of LDH into the coronary effluent in both WT and deletion compared to time control (d). However, LDH release was decreased in CPNS1 deletion mice compared to WT during reperfusion (d). These results supported that deletion of CPNS1 decreased cardiac injury during ISC–REP. Data are expressed as mean ± SD; *p < 0.05 vs. time control; †p < 0.05 vs. corresponding WT.