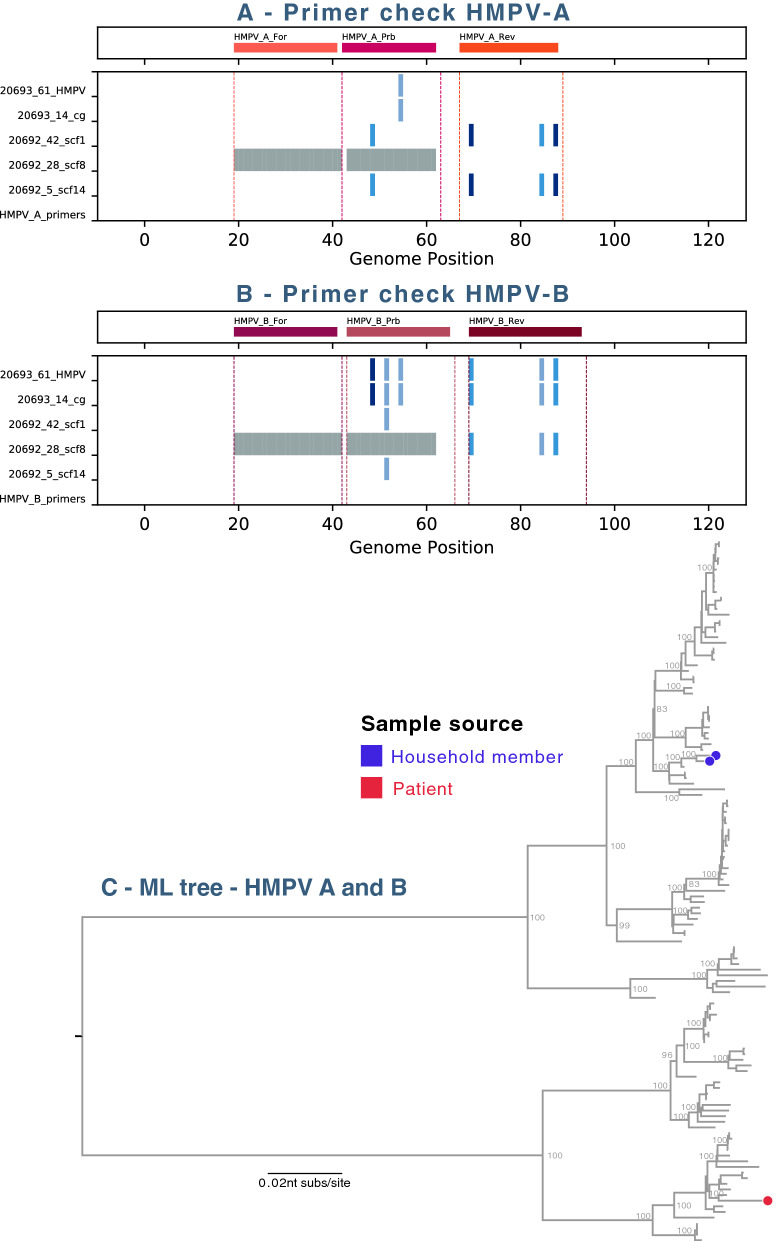
Figure 1.
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) identified in the study. (A) The diagnostic primers and probe target sites in the Kilifi HMPV genotype A genomes and contigs were examined. All viral contigs from each virus family or type were aligned using MAFFT25, and the alignment was trimmed to a 100–200 nt region surrounding the primer and probe target sites. Nucleotide differences between the expected primer and probe target sites and the actual contig sequences were identified and plotted in shades of blue and gaps in contig sequences were indicated in grey. (B) As in (A) but for HMPV genotype B. (C) Maximum-likelihood (ML) phylogenetic tree of HMPV genomes. Local strains on the phylogenetic tree were indicated by circles coloured in blue indicating household member and in red indicating KCH patients. The tree was mid-point rooted for clarity and horizontal branch lengths were drawn to the scale of nucleotide substitutions per site. The tree comparing local HMPV genomes to global genomes suggested that the local HMPV belonged to genotype A2 and B1.