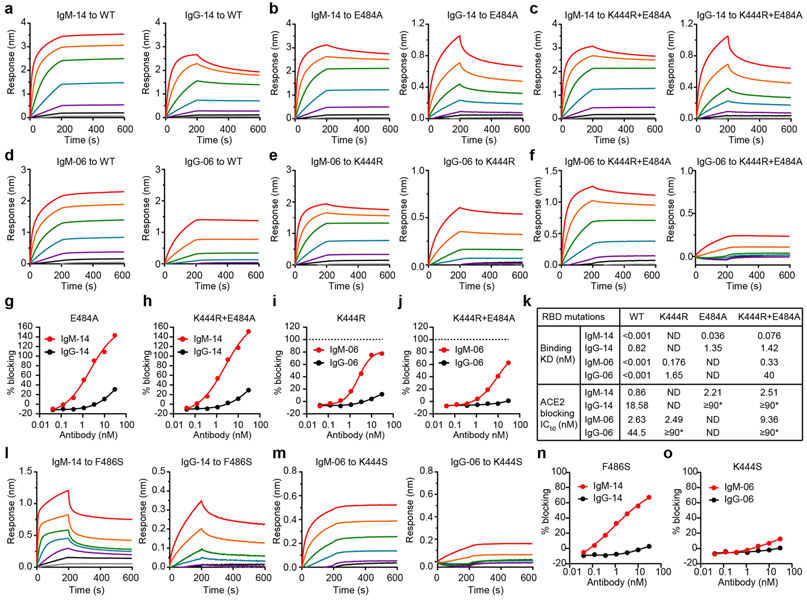
Extended Data Fig. 6 ∣. Binding kinetics and ACE2-blocking activities of IgM-14, IgG-14, IgM-06 and IgG-06 against selected RBD mutants.
a–c, The binding kinetics of IgM-14 and IgG-14 to wild-type RBD (a), E484A RBD (b) and K444R + E484A RBD (c). d–f, The binding kinetics of IgM-06 and IgG-06 to wild-type RBD (d), K444R RBD (e) and K444R+E484A RBD (f). g, h, IgM-14 and IgG-14 blocking of E484A RBD (g) and K444R + E484A RBD (h) interaction with ACE2. i, j, IgM-06 and IgG-06 blocking of K444R RBD (i) and K444R + E484A RBD (j) interaction with ACE2. k, Summary of the binding avidities (KD) and ACE2-blocking activities (IC50) to indicated RBD proteins by IgM-06 and IgG-06. ND, not determined. *Half-maximal blocking was not achieved at the highest monoclonal antibody concentration (30 nM) and the IC50 values are defined as ≥90 nM. l, m, The binding kinetics of IgM-14 and IgG-14 to F486S RBD (l) and IgM-06 and IgG-06 to K444S RBD (m). n, o, IgM-14 and IgG-14 blocking of F486S RBD interaction with ACE2 (n) and IgM-06 and IgG-06 blocking of K444S RBD interaction with ACE2 (o).