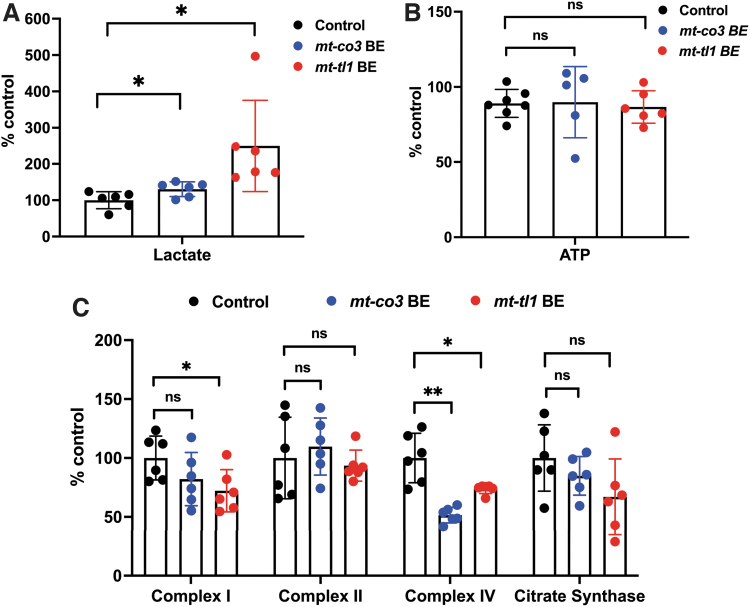
FIG. 9.
Functional consequence of base edits in mtDNA in zebrafish larvae. (A-B) Zebrafish larvae injected with mt-co3 and mt-tl1 BE RNAs raised to 7 dpf were collected and homogenized in 0.5 M perchloric acid and used for lactate (A) and ATP (B) assays. (A) Lactate concentrations in the samples were quantified (20 larvae each replicate: N = 6). Larvae injected with mt-co3 and mt-tl1 RNA displayed significant elevated lactate levels compared with the control (p < 0.05). Each data represent one biological replicate and error bars are represented as standard deviation. (B) No significant difference was observed in the steady-state ATP levels of larvae injected with the BE RNAs for mt-co3 and mt-tl1 genes compared with control larvae (p > 0.05) (N = 5 for mt-co3 and N = 6 for mt-tl1). ATP levels were maintained for both the groups. (C) For the mitochondrial respiratory chain complex activities, 20 larvae each tube were homogenized in the mitochondrial isolation buffer (250 mM sucrose, 20 mM Tris-HCl, 3 mM EDTA, pH 7.4) followed by differential centrifugation (to enrich mitochondrial fraction), and an assay was performed (N = 6 biological replicates of 20 pooled 7 dpf zebrafish larvae). Slight decrease in the complex I enzyme activity was observed for both mt-co3 and mt-tl1 BE groups compared with the control larvae, whereas activity for the complex II was maintained across all the three groups. For complex IV, a significant decrease in the activity was observed for both sets of larvae injected with mt-co3 and mt-tl1 BE RNA compared with the control. No difference in the citrate synthase activity was observed between the injected and control larvae (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01). p-Values were determined by Student's t-test. Error bars represent the standard deviation. dpf, days postfertilization. Color images are available online.