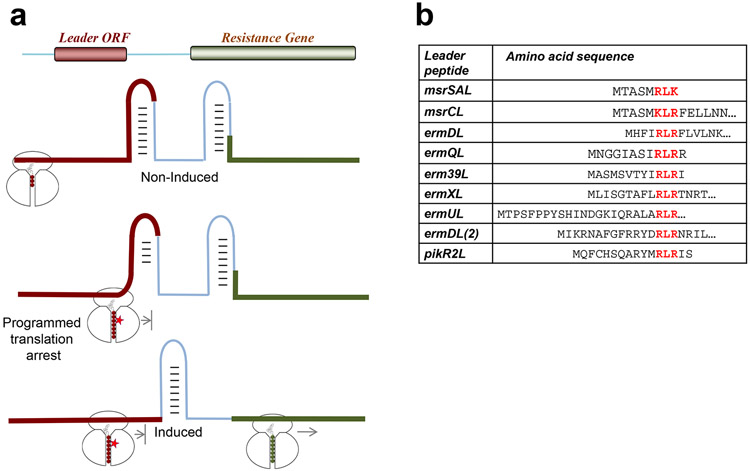
Figure 7.
Activation of antibiotics resistance genes relies on the context-specific action of ribosomal-targeting antibiotics. (a) Programmed translation arrest at the leader ORF mediates the change in mRNA conformation necessary to activate expression of the resistance gene. (b) Many of the regulatory peptides responsible for activating macrolide resistance genes contain the sequence motif +x+, a prevalent arrest motif for macrolide antibiotics.