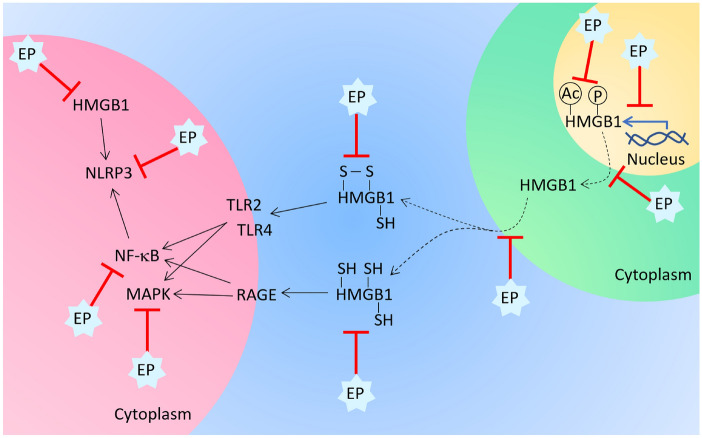
Fig. 1.
Effects of EP on signaling in immune cells and on HMGB1. EP affects HMGB1 on multiple levels. It reduces HMGB1 mRNA expression, HMGB1 translocation from the nucleus into the cytoplasm, phosphorylation and acetylation of HMGB1, and its release from the cells. Also, EP influences the HMGB1 redox status, as it modulates the reduction of HMGB1 cysteines. Depending on the cysteine reduction state, HMGB1 acts through RAGE or TLR to stimulate NF-κB and MAPK signaling, and these signaling pathways can also be inhibited by EP. TLR engagement by HMGB1 leads to activation of NLRP3 inflammasome. NLRP3 is also activated by intracellular HMGB1. EP is able to inhibit both ways of NLRP3 activation