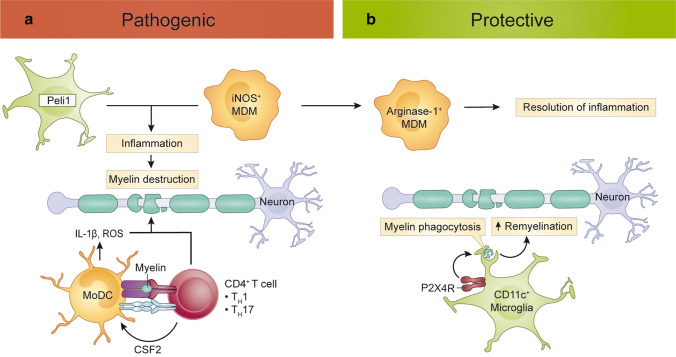
Fig. 5.
Protective and pathogenic roles of monocytes and microglia in autoimmune neuroinflammation. a Pathogenic functions. Peli-mediated microglial expression of pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokines can exacerbate inflammatory damage to myelin. GM-CSF-stimulated moDC activate myelin-reactive T cells and exacerbate myelin damage via the production of ROS and IL-1β. iNOS+ MDM producing ROS and NO contribute to myelin destruction but may also transition to arginase-1+ MDM and facilitate the resolution of inflammation (b). b Protective functions. Microglia may stimulate re-myelination via P2X4R-mediated phagocytosis of myelin debris. GM-CSF granulocyte–macrophage stimulating factor; IL interleukin; iNOS inducible nitric oxide synthase; MDM monocyte-derived macrophage; MHC major histocompatibility complex; moDC monocyte-derived dendritic cell; NO nitric oxide; P2X4R P2X purinoceptor 4; Peli Pellino E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase; ROS reactive oxygen species; TH T helper cell