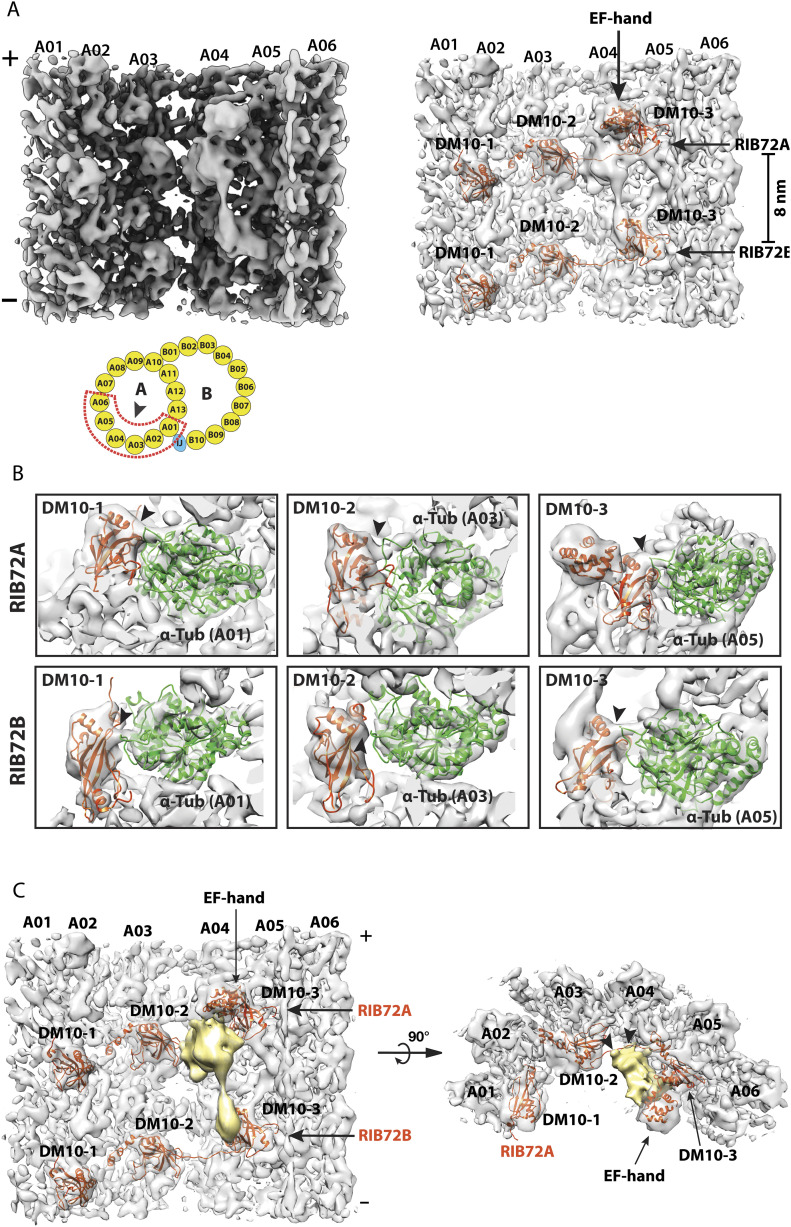
Figure 2. Structure of the 16-nm repeat of the doublet microtubule focusing on the RIB72A and RIB72B binding region.
(A) A side view of the density map focusing on the RIB72A/B binding sites. Left: the map is viewed from the luminal side of DMT as indicated by an arrowhead in the cartoon. Right: pseudo-atomic models of RIB72A and RIB72B, based on the structure from Chlamydomonas, are fit into the density map. The six DM10 domains and an EF-hand motif in the RIB72A C terminus are indicated. In the cartoon, the red dashed lines outline the structure feature used for focused local refinement. This includes the protofilaments A01∼A06 and their associated microtubule inner proteins (MIPs). (B) The DM10 domains bind to the K40 loops at the luminal side of α-tubulin. The models for the DM10 domains (in red) are fit into the density map. The α-tubulins are in green. The black arrowheads indicate the connecting densities and the potential interactions between the DM10 domain and the K40 loop from α-tubulin. The top row shows three DM10 domains from RIB72A. The bottom row shows three DM10 domains from RIB72B. (C) An unidentified MIP (in gold) crosslinks the C terminus of RIB72A and RIB72B. The averaged density map is shown in two orthogonal views. The black arrowheads indicate the binding sites of the unidentified MIP to the linker between DM10-2 and DM10-3 from RIB72A and to protofilament A04.