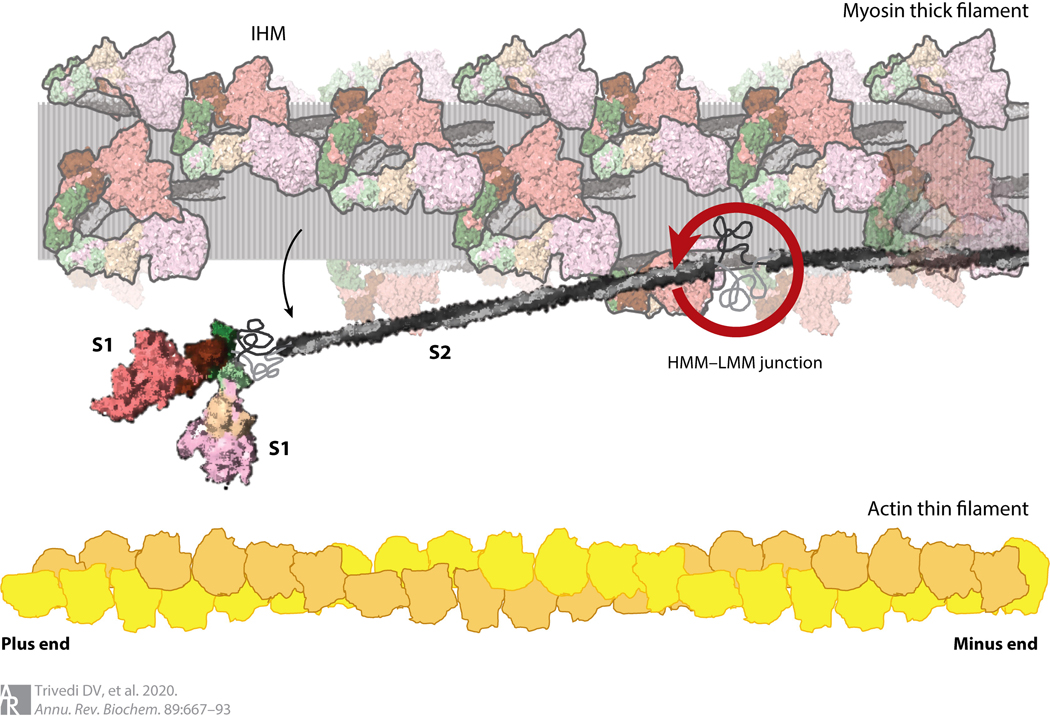
Figure 2.
Structure of cardiac myosin and arrangements in the muscle sarcomere drawn to scale. The HMM domain of the myosin consists of the two S1 domains and the S2 domain. LMM is the C-terminal portion of the coiled-coil tail to the right of the HMM–LMM junction. Interactions between the LMM portions of myosin molecules form the shaft of the thick filament. The relative sizes and spacings of the myosin-containing thick filament and the actin-containing thin filament within the muscle sarcomere are shown. The heads folded back onto the shaft of the thick filament are illustrated in their IHM state, with the S1 heads folded back onto their S2 tails (translucent myosins). A single myosin molecule released from its IHM state is shown swinging away from the thick filament, swiveling about its HMM–LMM junction. Abbreviations: HMM, heavy meromyosin; IHM, interacting heads motif; LMM, light meromyosin; S1, subfragment 1; S2, subfragment 2.