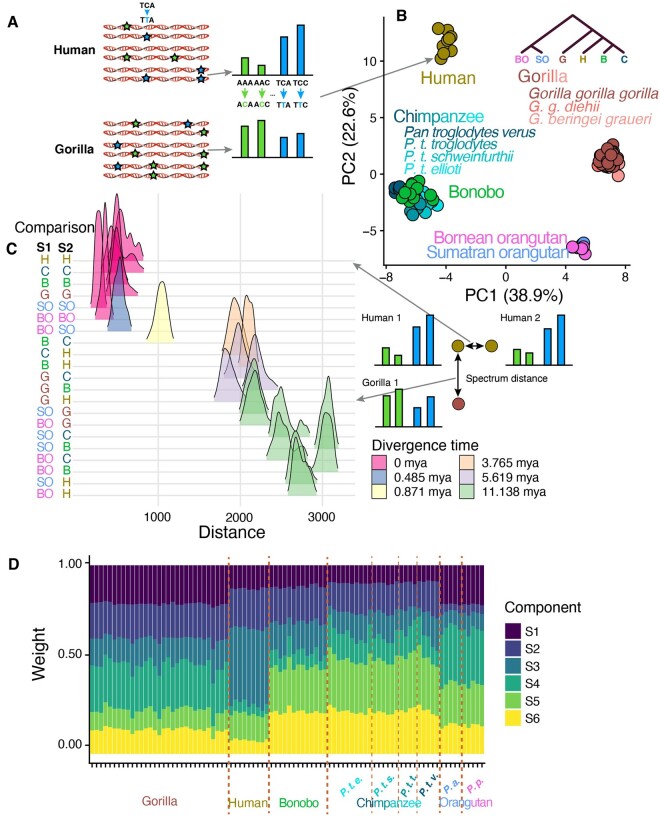
Fig. 1.
Covariance of species-specific and replication timing mutation spectra in great apes. (A) SNVs segregating within a species were counted to generate a triplet mutation spectrum for each individual in the GAGP. We include SNVs found in NCNR regions of the genome, which we collectively call the NCNR compartment. (B) PCA of NCNR compartment mutation spectra reveals clustering of individuals by species. Each point represents the NCNR compartment mutation spectrum from a single individual in the GAGP; colors represent species, whereas shades of a color represent subspecies (applies only to gorillas and chimpanzees). (C) Mutation spectra are more similar between individuals of the same species than between individuals from different species. We plotted the Euclidean distances between triplet mutation spectra of all possible pairs of individuals in the GAGP within and between species (see Materials and Methods). (D) When NMF is used to infer mutational signatures that best explain variation among ape mutation spectra, we see more variation of signature composition between species than within species and identify signatures that change in dosage on specific phylogenetic tree branches. For example, signature 1 appears to have decreased in dosage on the branch ancestral to humans, chimps, and bonobos.