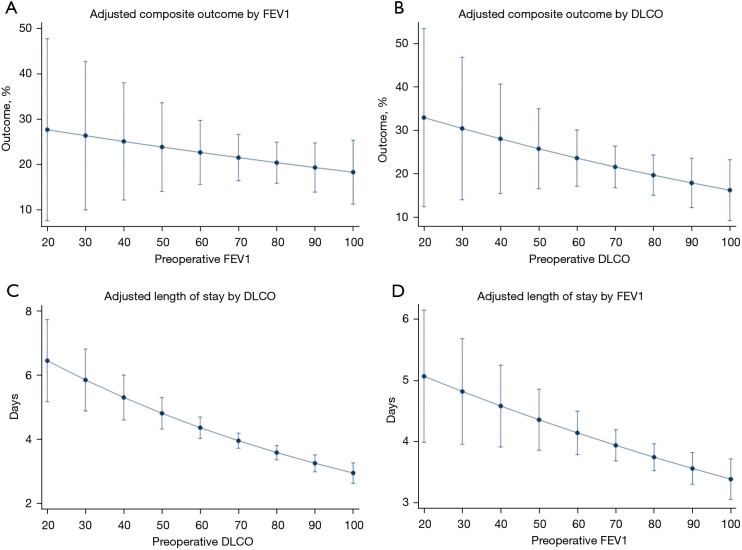
Figure 1.
Adjusted composite outcome and length of stay by FEV1 and DLCO. (A) Ninety-day composite respiratory outcome by deciles of FEV1. (B) Ninety-day composite respiratory outcome by deciles of DLCO. (C) Adjusted length of stay by deciles of DLCO. (D) Adjusted length of stay by deciles of FEV1. Note that FEV1 and DLCO are not significantly associated with the composite outcome, but are associated with length of stay. DLCO has a stronger association than FEV1. FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; DLCO, diffusion lung capacity of carbon monoxide.