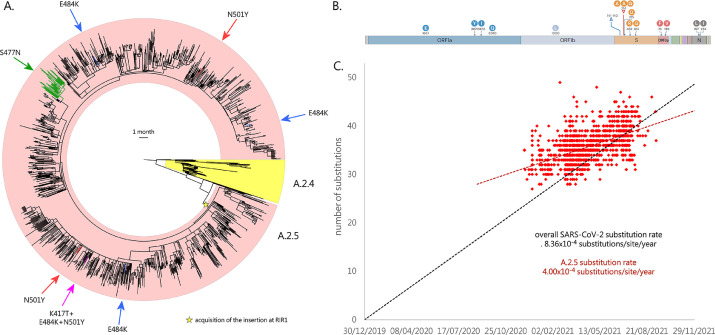
Fig. 3.
Panel A: circular time tree exemplifying the phylogeny of the A.2.5 lineage related sublineages. Only high quality, complete genomes have been included. The Wuhan-Hu-1 strain was used to root the tree; the sister lineage A.2.4 is also indicated. The acquisition of relevant spike mutations placed in the receptor binding domain (i.e. S477N, K417T, E484K and N501Y) is marked with arrows. Please note that the monophyletic clade linked with the acquisition of S477N corresponds to the A.2.5.3 sublineage. Panel B: key mutations associated with the A.2. lineages. Genes associated with mutations (compared with the reference strain Wuhan-Hu-1) are indicated; only mutations detected in > 50% of the genomes belonging to this lineage and associated sublineages are shown. Modified from https://outbreak.info/. Panel C: root-to-tip genetic distance (number of nucleotide substitutions) of the genomes belonging to the A.2.5 lineage and related sublineages, compared with the reference genome Wuhan-Hu-1. The black dashed line represents the average rate of mutation of all SARS-CoV-2 sequenced genomes, according to GISAID (i.e. 25 substitutions per genome per year, as of January 5th, 2022). The red dashed line represent the rate of mutation computed for A.2.5. Note that insertions and deletions were excluded from this calculation.