FIGURE 4.
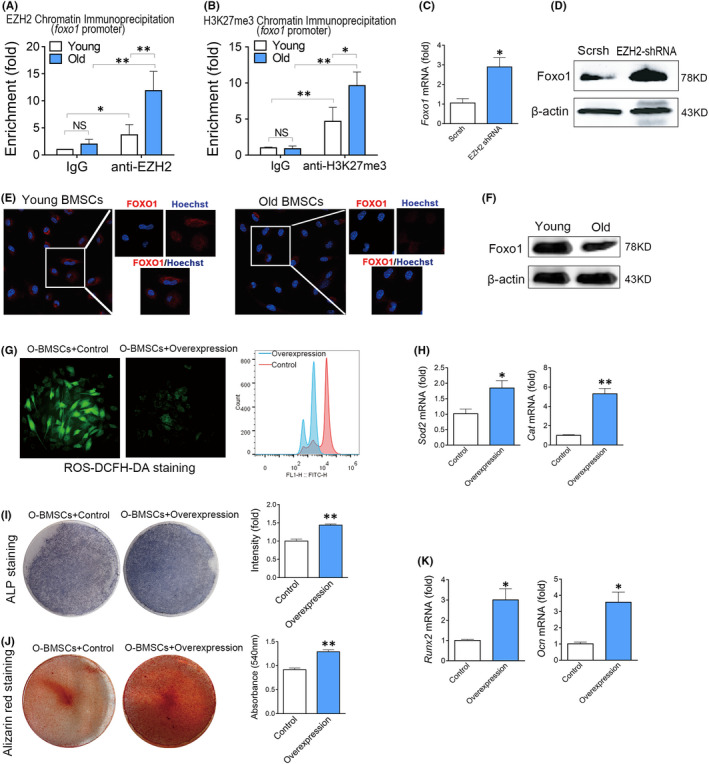
Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 suppresses Foxo1‐mediated antioxidant defence. (A) CHIP analysis of the binding of EZH2 at the promoter region of the Foxo1 gene. n = 4. (ANOVA) (B) CHIP analysis of the binding of H3K27me3 at the promoter region of the Foxo1 gene. n = 4. (ANOVA) (C) Real‐time RT‐PCR analysis of Foxo1 in BMSCs transfected with EZH2 shRNA or Scrsh for 48 hr. n = 3. (t test) (D) Western blot analysis of Foxo1 in BMSCs transfected with EZH2 shRNA or Scrsh for 48 hr. (E) Immunofluorescence assay of Foxo1 expression in young or old BMSCs. (F) Western blot analysis of Foxo1 expression in young or old BMSCs. (G) Fluorescence analysis of ROS levels in BMSCs transfected with Foxo1‐lentivirus or negative control. (H) Real‐time RT‐PCR analysis of Sod2 and Cat mRNA levels in BMSCs transfected with Foxo1‐lentivirus or negative control. n = 3. (t test) (I) ALP staining of BMSCs transfected with Foxo1‐lentivirus or negative control after 7 days of osteogenic induction. n = 3. (t test) (J) Alizarin red staining of BMSCs transfected with Foxo1‐lentivirus or negative control after 14 days of osteogenic induction. n = 3. (t test) (K) Real‐time RT‐PCR analysis of Runx2 and Ocn mRNA levels in BMSCs transfected with Foxo1‐lentivirus or negative control after 14 days of osteogenic induction. n = 3. (t test) Data are shown as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. NS, no significance
