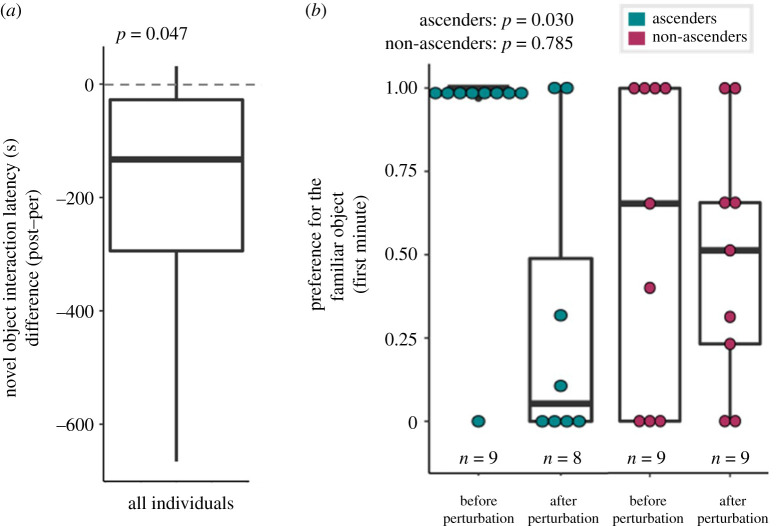
Figure 3.
After social perturbation, all males approached the novel object more quickly compared to pre-perturbation baselines (p = 0.047) (a). Ascending males significantly decreased preference for the familiar object when reassessed in the novel object recognition task following social ascent (p = 0.030) (b, left), whereas non-ascending males did not (p = 0.785) (b, right). (Online version in colour.)