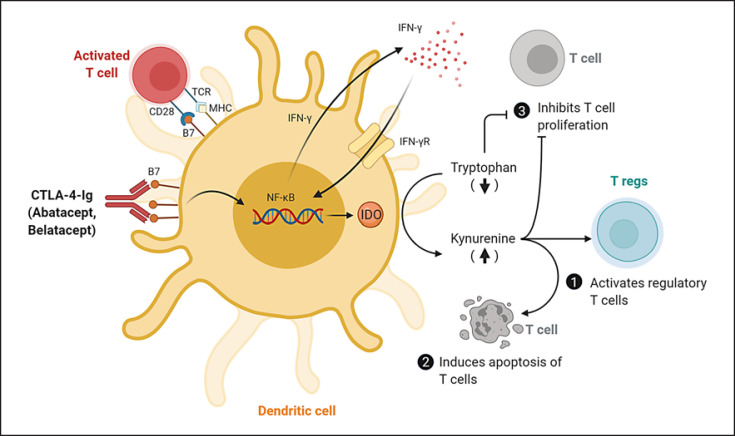
Fig. 3.
KP activation by CTLA-4-Ig in dendritic cells and their effects on T lymphocytes. CTLA-4-Ig engages B7 receptor on dendritic cells to induce the production of IFN-γ and promote the upregulation of IDO and activation of KP. This leads to an accumulation of the KP metabolites and a depletion of TRP, which can activate Tregs (1), induce apoptosis of T cells (2), and inhibit the proliferation of T cells (3). B7, B7 costimulatory molecule; CTLA-4-Ig, Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4-immunoglobulin; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; IFN-γ, interferon-gamma; IFN-γR, interferon-gamma receptor; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Tregs, regulatory T cells; TCR, T-cell receptor; KP, kynurenine pathway; TRP, tryptophan. (Adapted from Finger and Bluestone [200] and created with BioRender.com.)