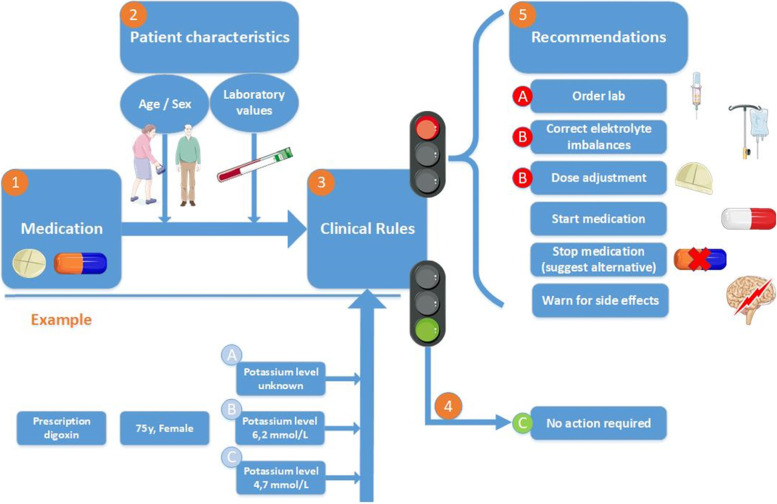
Fig. 2.
Schematic overview of the CDSS and example. Legend: When running the CDSS, the patient’s medication list (1) is combined with his/her characteristics (2), such as age, sex and laboratory values (renal function, potassium level etc.). Next, these data are run through the 225 different clinical rules (3). When no clinical rules apply, a green signal is given (4) and no further actions are required (C). When clinical rules do apply a red signal is given and clinical recommendations (5) will be sent to the GP and/or pharmacist. The figure also shows an example of a 75 year-old female that is prescribed digoxin. The clinical rule about ‘potassium and digoxin’ is applied and different scenario’s in which the potassium level is unknown (A), 6.2 mmol/L (B) or 4.7 mmol/L (C) lead to different clinical recommendations with the recommendation to order lab (A), correct electrolyte imbalances or dose adjustment (B) or no action is required (C), respectively. This figure was created using Servier Medical Art templates, which are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License; https://smart.servier.com