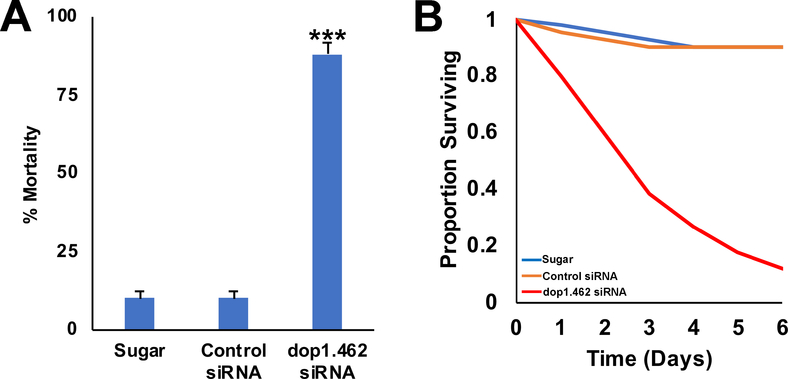
Fig. 3. Delivery of dop1.462 siRNA as an ATSB results in high levels of A. aegypti adult mortality.
A. In simulated field trials, high levels of adult mortality were observed in adult females that fed on ATSB with 2.5 μg/μl dop1.462 siRNA (n=34) vs. sugar bait alone (Sugar; n=41) or sugar bait with 2.5 μg/μl control siRNA (Control siRNA, n=41). The average dose was ~12 μg siRNA per mosquito. The data shown, which were compiled from three biological replicates trials, are represented as mean percentage mortality and were analyzed using the log-rank test; error bars represent SEM; ***=P<0.001 in comparison to sugar alone or control siRNA treatments. B. The survival curves over a six day trial period are shown for adult females that fed on sugar bait, control siRNA sugar bait, or dop1.462 ATSB.