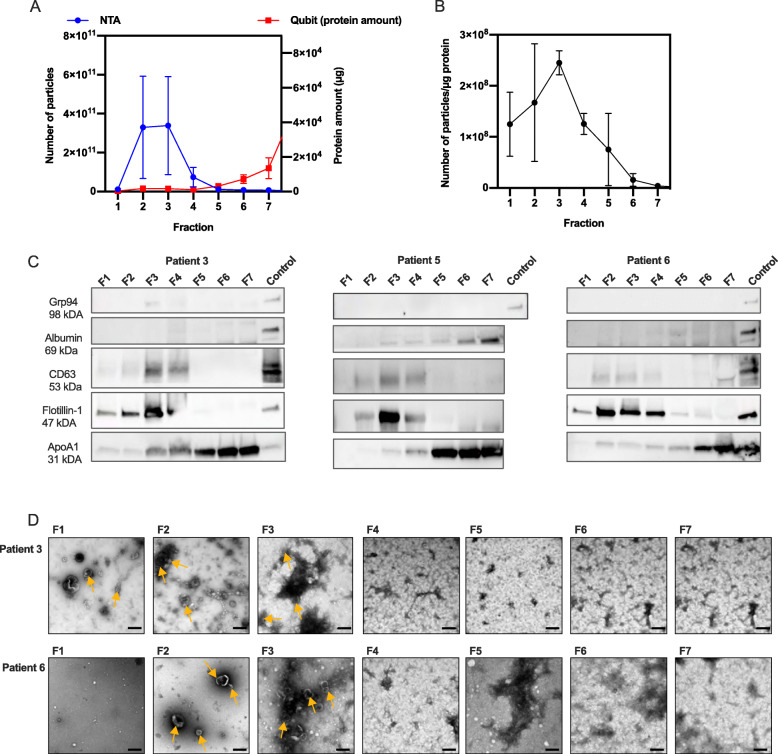
Evaluation of EV enriched fractions after SEC isolation of EVs from lymphatic drainage fluid from breast cancer patients. EVs were isolated from lymphatic drainage fluid of three patients (patient 3, 5 and 6) collected 1 day after breast surgery using qEV SEC. Seven fractions were collected, concentrated using ultrafiltration and analyzed. A Total particle number and protein amount and B particle to protein ratio in each of the 7 fractions analyzed by NTA and protein quantification by Qubit. C Fraction 1–7 (F1–7) were analyzed further by western blot (loading 20 μg except for F1 in patient 4 and 6 where the maximum volume was loaded (2.5 and 3.4 μg respectively) due to low protein concentration) detecting the EV markers Flotillin and CD63, endoplasmic reticulum marker Grp94, lipoprotein ApoA1 and albumin. EV proteins Flotillin and CD63 were mainly localized in F2–4, and non-EV proteins ApoA1 in F5–7. Albumin and Grp94 were not detected in any of the fractions. The positive control used was proteins extracted from MSC cell lysate (Grp94 and Flotillin-1), EVs from mesenchymal stem cells (CD63), human melanoma metastatic tissue (albumin and ApoA1). Western blot membranes are cropped, uncropped membranes are shown in Additional file 7. D TEM images of qEV fractions 1–7, patient 3 and 6. Size bar; 200 nm. Some of the vesicle-shaped particles are indicated by yellow arrows. EVs were mainly present in F1–3, while in F4–7, smaller, lipoprotein-like particles were covering most of the TEM grid. Values are mean values of the three patients and error bars indicates standard error of the mean

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.