Fig. 3.
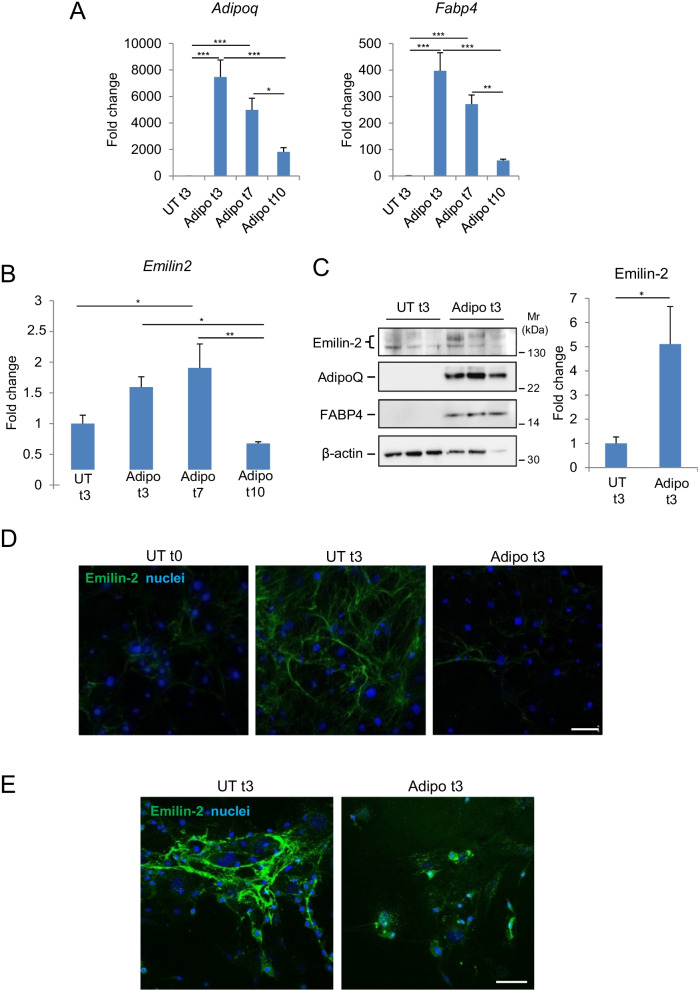
Emilin-2 expression during in vitro adipogenic differentiation of primary BM-MSC. A, B RT-qPCR analysis of the mRNA levels for the adipogenic markers AdipoQ (A, left) and FABP4 (A, right) or for Emilin-2 (B) in primary murine BM-MSC under non-differentiating conditions (UT t3) or treated for 3, 7 and 10 days with adipogenic stimuli (Adipo t3, t7 and t10). mRNA levels are shown as fold change compared to UT t3 condition (n = 6; *P < 0.05;**P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). C Western blot analysis for Emilin-2, AdipoQ and FABP4 proteins in primary murine BM-MSC under non-differentiating conditions (UT t3) and after 3 days of adipogenic differentiation (Adipo t3). Three independent samples are shown for each condition. β-actin was used as a protein loading control. The graph on the right show the densitometric quantification for Emilin-2, as determined by two independent experiments. Protein levels are shown as fold change compared to UT t3 condition (n = 4; *P < 0.05). D Representative immunofluorescence for Emilin-2 (green) in primary murine BM-MSC cultures in control conditions (UT t0) and after 3 days in non-differentiating (UT t3) or adipogenic differentiating (Adipo t3) conditions. Scale bar, 100 μm. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). E Immunofluorescence for Emilin-2 (green) in primary murine BM-MSC cultures maintained for 3 days in non-differentiating (UT t3) or adipogenic differentiating (Adipo t3) conditions, and subjected to permeabilization with Triton X-100 before immunostaining. In non-differentiating conditions, most Emilin-2 labeling is found in the ECM in the form of an organized fibrillar network, whereas in cultures subjected to adipogenic differentiation Emilin-2 reactivity is found inside the cells in the form of dots scattered throughout the cytosol. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar, 100 μm. See also Additional file 1: Figs. S1, S2 and S3