Extended Data Figure 1 |. Histological validation of implanted sites.
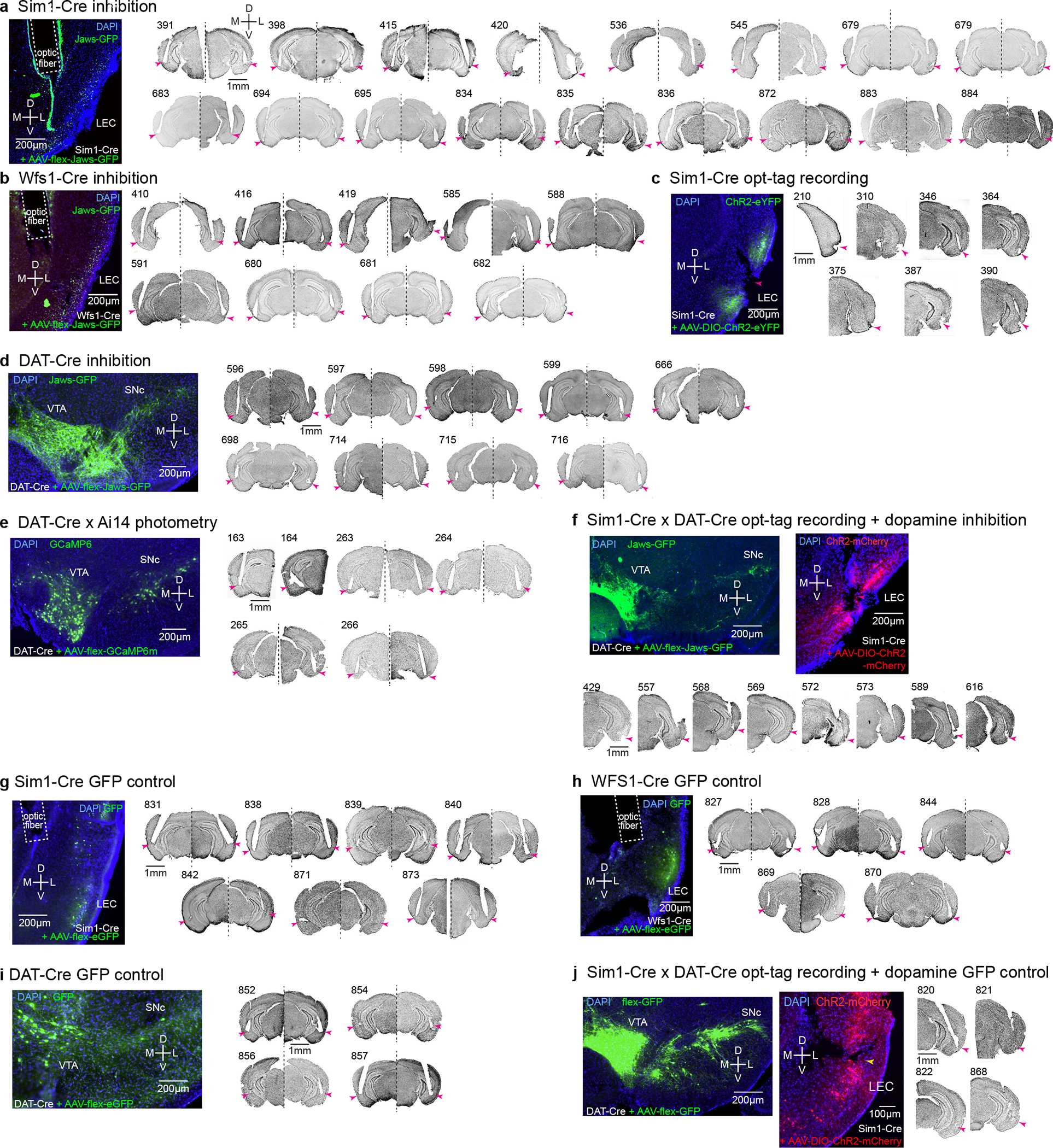
(a) Optic fiber positions in the LEC of Sim1-Cre mice injected with AAV-flex-Jaws-GFP for inhibition experiments. Arrowhead, the tip of optic fibers. D, dorsal, V, ventral, M, medial, L, lateral.
(b) Optic fiber positions in the LEC of Wfs1-Cre mice for inhibition experiment of Wfs1-expresing pyramidal cells.
(c) Recording position in the superficial layer of LEC from Sim1-Cre mice for opt-tagging experiment. Note large lesions because of the electrical lesioning.
(d) Optic fiber positions in the LEC of DAT-Cre mice injected with AAV-flex-Jaws-GFP in the VTA/SNc for inhibition experiment.
(e) Optic fiber positions in the LEC of DAT-Cre x Ai14 mice for photometry experiment. Two mice received unilateral implantations and four mice received bilateral implantations.
(f) Recording position in the superficial layer of LEC from Sim1-Cre x DAT-Cre mice for opt-tagging + inhibition experiment.
(g) Optic fiber positions in the LEC of Sim1-Cre mice injected with AAV-flex-GFP for control inhibition experiment.
(h) Optic fiber positions in the LEC of Wfs1-Cre mice injected with AAV-flex-GFP for control inhibition experiment.
(i) Optic fiber positions in the LEC of DAT-Cre mice injected with AAV-flex-GFP at VTA and SNc for control inhibition experiment.
(j) Recording position in the superficial layer of LEC from Sim1-Cre x DAT-Cre mice for opt-tagging (ChR2-mCherry) + control inhibition (GFP) experiment.
