Figure 1 |.
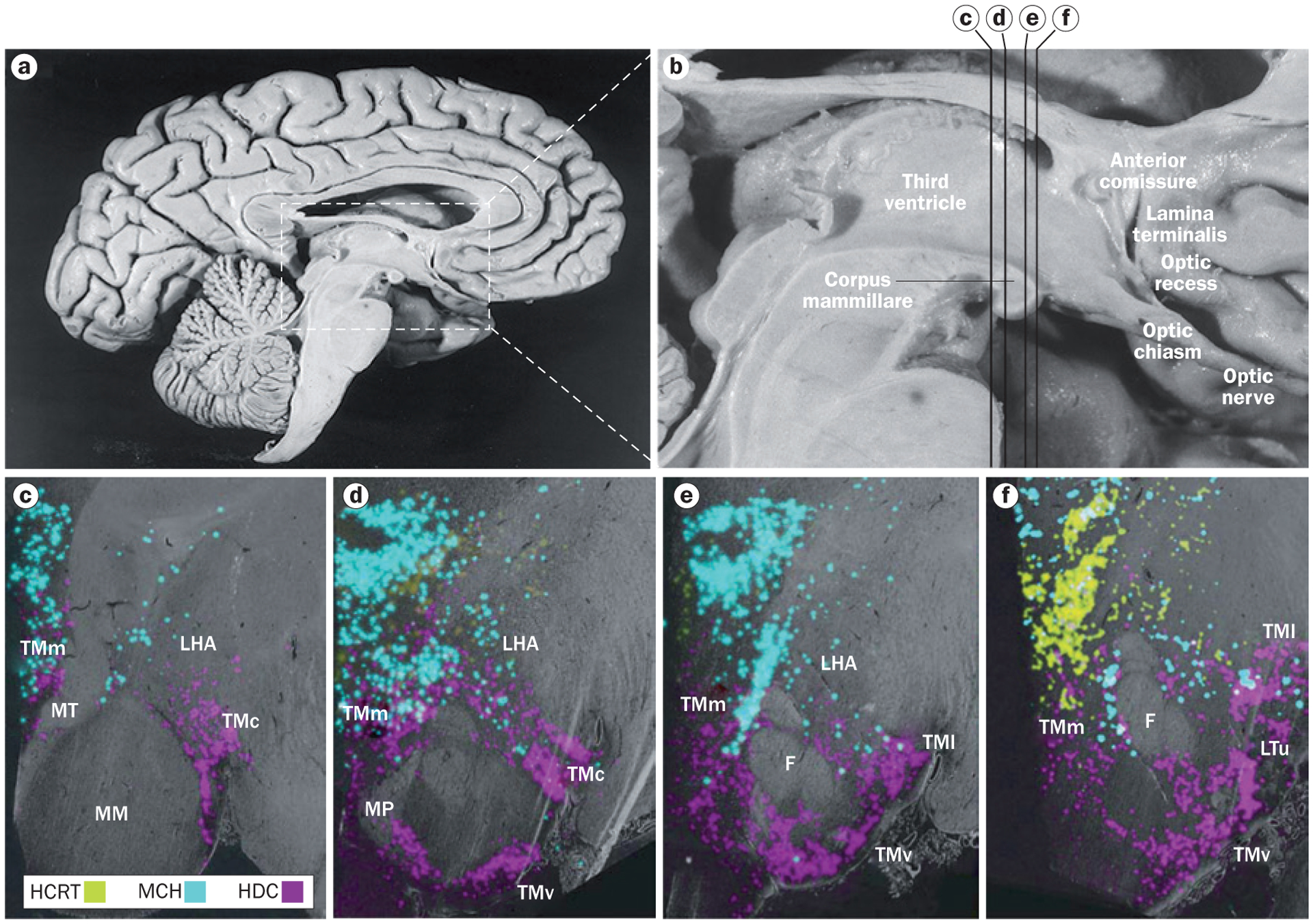
Neurons containing histamine, hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone in the human hypothalamus. a | Overview of the medial surface of the human brain, and b | detail of the hypothalamus. The distribution of neurons containing histamine, hypocretin and melanin-concentrating hormone are shown with in situ hybridization in coronal sections of hypothalamus at the c | posterior level through the medial mammillary nucleus, d | rostromammillary level at the principal mammillary fasciculus, e | level of the caudal end of the fornix and f | premamillary level. In panels c–f, the third ventricle is on the left side. Abbreviations: F, fornix; HCRT, hypocretin neurons; HDC, histidine-decarboxylase-positive (histamine) neurons; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; LTu, lateral segment of the lateral tuberal nucleus; MCH, melanin-concentrating hormone neurons; MM, medial mammillary nucleus; MP, mammillary peduncle; MT, mammillothalamic tract; TMc, caudal tuberomammillary nucleus; TMl; lateral tuberomammillary nucleus; TMm, medial tuberomammillary nucleus; TMv, ventral tuberomammillary nucleus. Panels a and b reprinted with permission from Elsevier © Handbook of Clinical Neurology Vol. 79. Swaab, D. F. The human hypothalamus: basic and clinical aspects. Part 1: Nuclei of the human hypothalamus 3–38 (2003). Parts c–f adapted with permission from John Wiley & Sons © Krolewski, D. M. et al. J. Comp. Neurol. 518, 4591–4611 (2010).
