Figure 4 |.
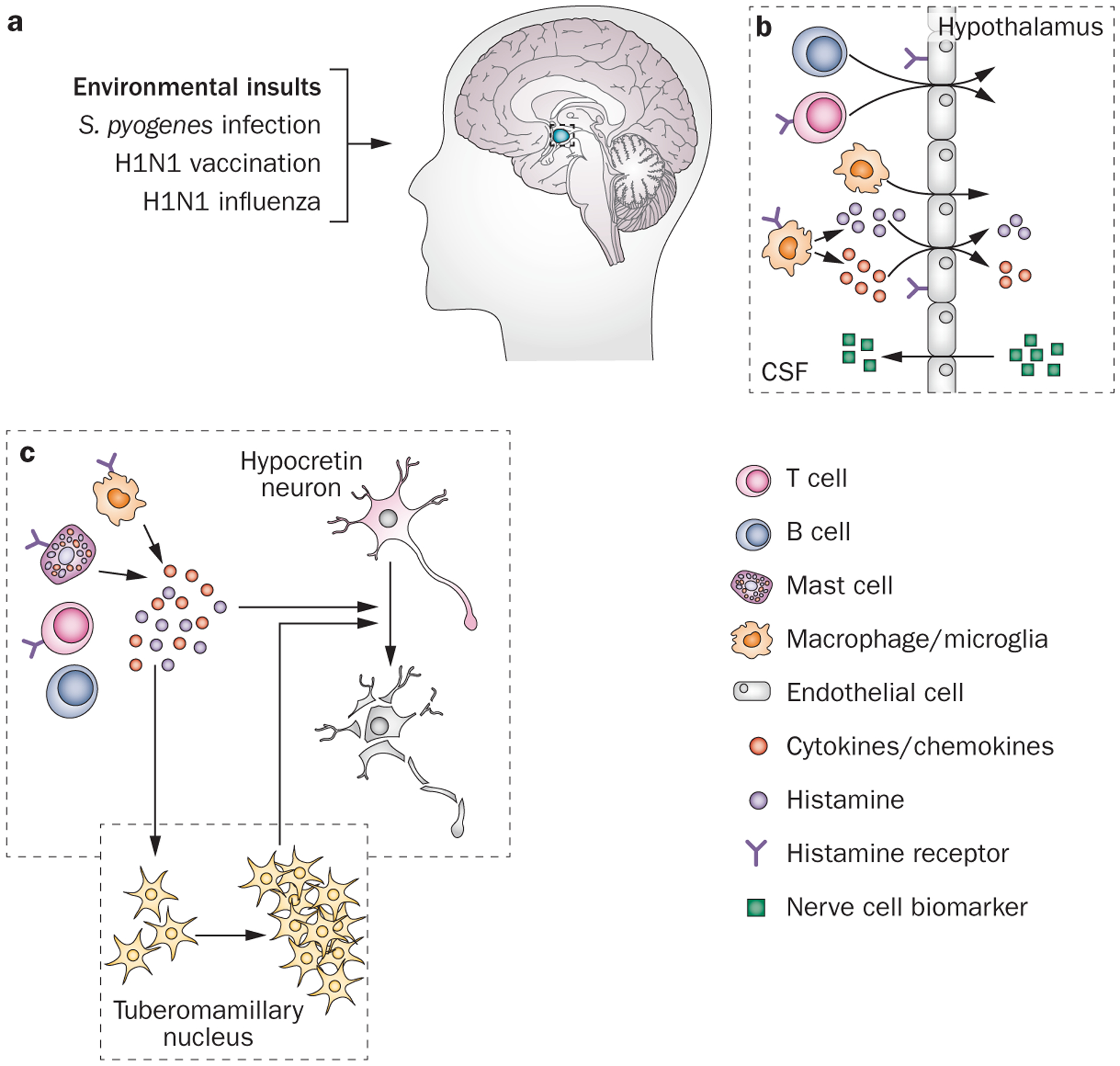
A schematic model of autoimmune-triggered histaminergic involvement in hypocretin neuron degeneration. a | The development of narcolepsy can sometimes be triggered by environmental factors, such as Streptococcus pyogenes infection, upper airway infection, H1N1 influenza or H1N1 vaccination with squalene-based adjuvant. Histaminergic signalling has a crucial role in several autoimmune diseases of the CNS. b | For example, binding of histamine to endothelial cell histamine receptors increases the permeability of the blood–brain barrier, (as indicated by increased levels of neuron-specific markers Aβ, total tau protein, phosphorylated tau, and neuro-specific enolase in the CSF), thereby facilitating T cell entry to the CNS.81–87 Moreover, histamine signalling enhances the activity of type 1 T helper cells through binding to histamine type 1 receptors located on these cells.88 c | T cells, B cells, macrophages, microglia and mast cells secrete histamine and other cytokines and chemokines,78,89,90,163 triggering a local inflammatory response that can damage the sensitive hypocretin neurons. Abbreviations: Aβ, amyloid-β; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid.
