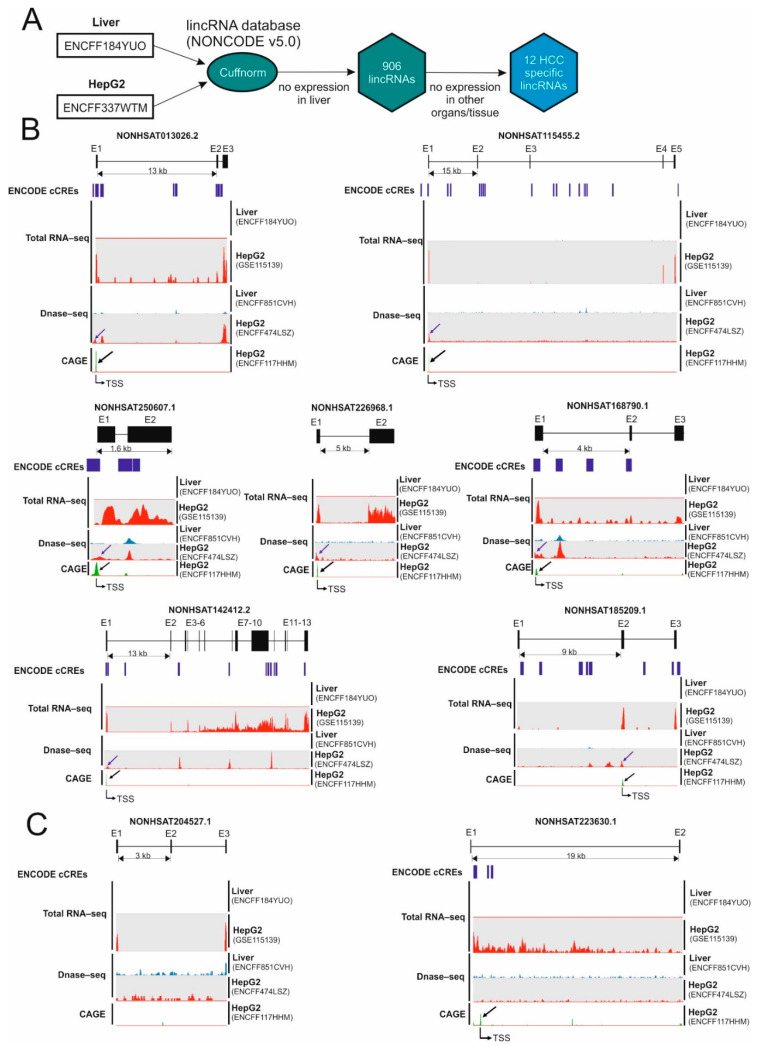
Figure 1.
Identification of hepatocellular carcinoma-specific lncRNAs. (A) RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) data from normal liver (ENCFF184YUO) and from the HCC cell line HepG2 (ENCFF337WTM) were aligned to the human reference genome (GRCh38) using Bowtie2. The gene expression values (Fragments per Kilobase Million (FPKM)) were calculated by Cuffnorm using the human NONCODE v5.0 transcript reference. A total of 906 long intergenic noncoding RNAs (lincRNAs) that were expressed in HepG2 cells but not in the normal liver were selected. Among these 906 lincRNAs twelve lincRNAs were expressed exclusively in HepG2 cells but not in the liver and other organs/tissues. (B,C) Abnormal chromatin structure induced expression of HCC-specific lincRNAs: Total RNA-seq from liver (ENCFF184YUO) and HepG2 cells (GSE115139), DNase-sequencing (DNase-seq) from normal liver (ENCFF851CVH) and HepG2 (ENCFF474LSZ) and candidate cis-Regulatory Elements (cCREs) generated by ENCODE consortium (ENCODE cCREs, blue mark) and cap analysis of gene expression (CAGE) data in HepG2 cells (ENCFF177HHM) were aligned to the human reference genome (GRCh38). SeqMonk was used to quantitate and visualize the data. Peaks in the wiggle plot represent the normalized RNA-seq, DNase-seq and CAGE read coverage on HCC-specific lincRNAs. E: exon; blue arrow: Open chromatin region at the putative promoter; black arrow: transcription start site (TSS) detected by CAGE.