Figure 2. AP-4-287 repressed germinal center formation & reduced Tfh CD4+ T cells in SRBC-vaccinated mice.
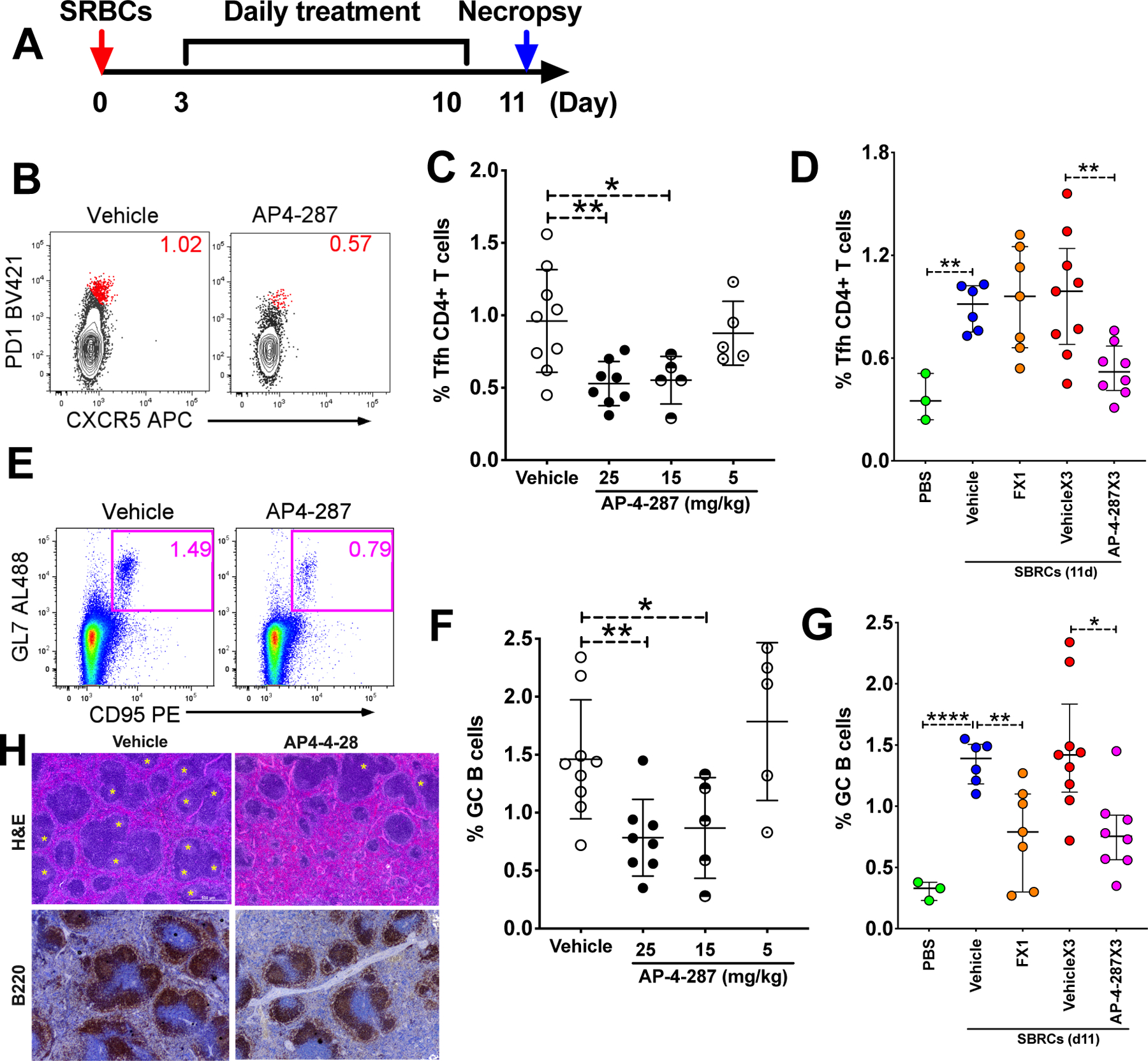
(A) Study design for evaluating AP-4-287 in repressing GC reaction in a sheep red blood cell (SRBC) vaccinated T cell-dependent mice model. All mice in the study received 100ul 10% SRBC i.p. on day 0 and underwent resting for 3 days. An 8-days course of AP-4-287 treatment (25mg/kg in 100uL vehicle three times daily with 5hr apart) or vehicle treatment started by day 4. By day 11, all mice were euthanized for collecting necropsy specimens including blood and spleen. (B) Representative flow plot showing AP-4-287 reduced the frequency of splenic PD1hiCXCR5+Tfh CD4+ T cells. (C) AP-4-287 reduced the frequency of Tfh CD4+ T cells in a dose-dependent manner. (D) Data obtained from cytometry analysis showed that the frequency of Tfh CD4 T cells in the mice receiving 80mg/kg FX1, or 25mg/kg AP4-287 or vehicle. (E) Representative flow plot showing AP-4-287 reduced GC B cells (B220+GL7+CD95+) in the spleen. (F) AP-4-287 reduced GC B cells in a dose-dependent manner. (G) Data obtained from cytometry analysis showed that the frequency of Tfh CD4 T cells in the mice receiving 80mg/kg FX1, 25mg/kg AP4-287 or vehicle. (H) Representative images (4x magnification) stained with H&E staining method and IHC using antibody against B220 showing AP-4-287 reduced GC formation in the spleens of SRBC-vaccinated mice. Welch-test was performed to compare the frequencies of Tfh and GC B cells between two groups. * p<0.05; ** p<0.01; ****p<0.0001. All data are from 2–3 independent experiments with 3 mice per experiment, except for PBS treatment in Figure C right and E right.
