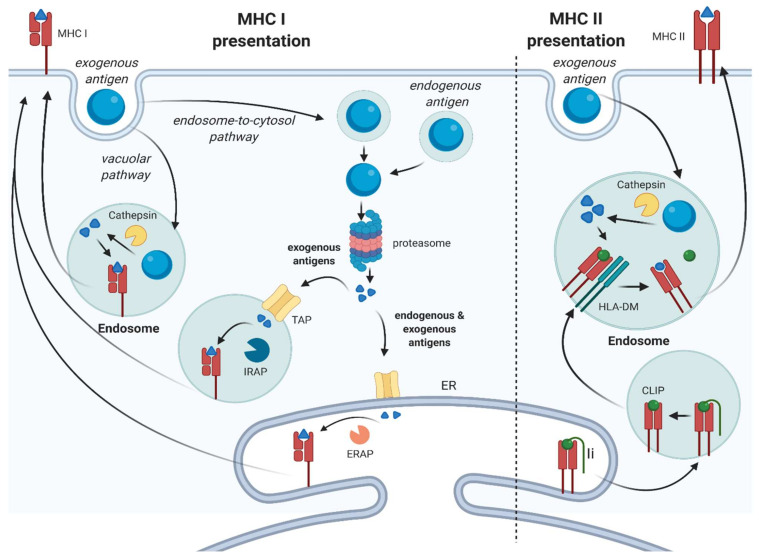
Figure 1.
Exogenous antigen processing. MHC I presentation: in the endosome-to-cytosol pathway, exogenous soluble and particulate antigens are processed by the proteasome and enter either the ER or the endosome via TAP and are further processed by ERAP or IRAP, respectively. Endogenous antigens are also processed by the proteasome in the cytosol and enter the ER. Then, the antigens are loaded on the MHCI. In the vacuolar pathway, the antigen is processed by cathepsin S and is loaded onto the MHCI in an endosome. MHC II presentation: the antigen is processed by cathepsins in the endosome after internalization. The MHCII molecule is formed in the ER and Ii is cleaved in the endosome, which leaves CLIP in the binding pocket of MHCII. In the endosome, CLIP is removed by HLA-DM, so the antigen can bind. ER: endoplasmic reticulum; Ii: invariant chain; CLIP: class II-associated invariant chain peptide; TAP: transporter associated with antigen processing; IRAP: insulin-regulated aminopeptidase; ERAP: endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase; MHC: major histocompatibility complex.