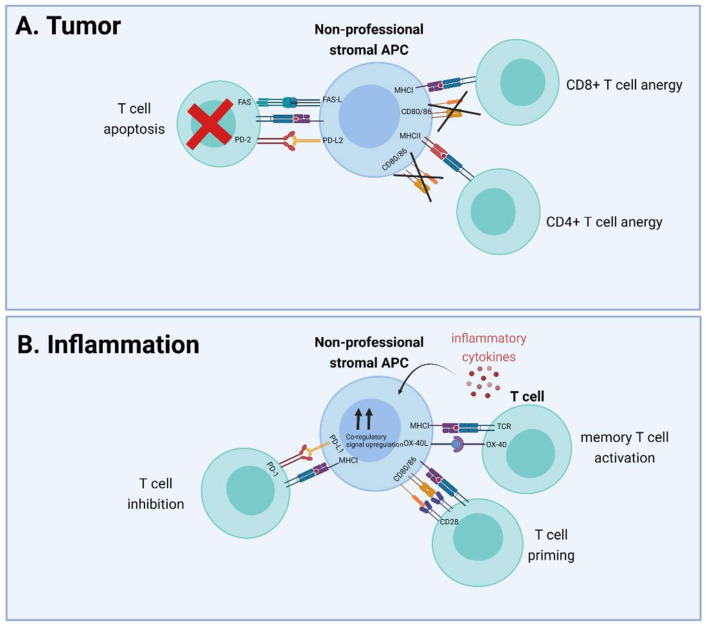
Figure 2.
Effect of nonprofessional stromal APC antigen presentation on T cell function in tumor and inflammatory conditions. (A) CAFs reside in the tumor micro-environment, cross-present exogenous antigen cells to CD8+ T cells, and delete them in a PD-L2- and FAS-L-dependent manner, or cause anergy in T cells after antigen presentation by either MHCI or MHCII due to the lack of co-stimulatory molecules. (B) Inflammation results in the release of inflammatory cytokines that can cause upregulation of co-stimulatory (CD80, CD86, OX-40L) or co-inhibitory (PD-L1) molecules. Predominant upregulation of co-stimulatory signals enables T cell priming (CD28-CD80/86) interaction and memory T cell activation (OX-40L-OX-40) by nonprofessional stromal APCs, while upregulation of PD-L1 results in T cell inhibition. APC: antigen-presenting cell; PD-L: programmed death-ligand; TCR: T cell receptor; MHC: major histocompatibility complex; FASL: FAS ligand.