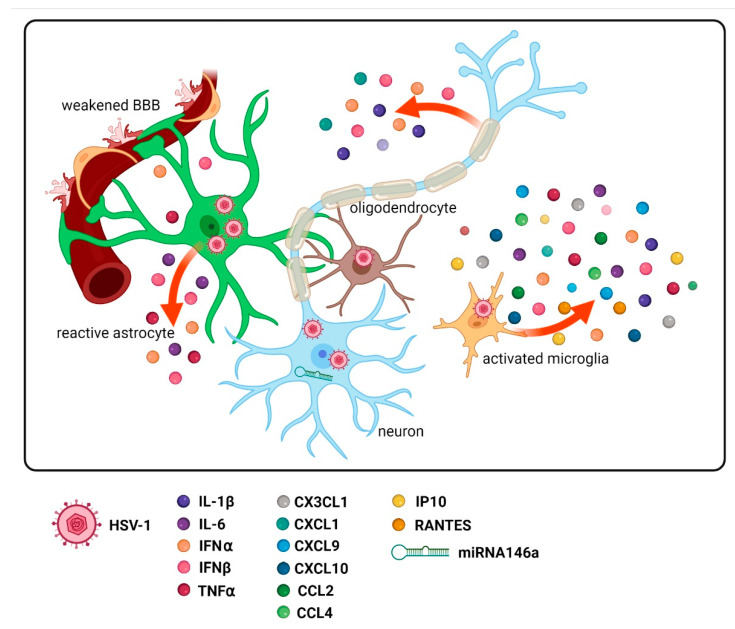
Figure 2.
Induction of specific cytokines and chemokines secretion by CNS cells following HSV-1 infection. After HSV-1 entry into the brain, neurons, as well as glial cells, become infected. The BBB becomes weakened [80] and HSV-1 infection leads to the activation of astrocytes, which produce pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IFN-α, IFN-β, TNFα, and IL-6 [81,82]. Activated microglia secrete IFN-α, IFN-β, IL-1β, IL-6, TNFα, IP-10, CXCL10, CCL2, CCL4, CX3CL1, CXCL9, and CCL5 (RANTES) [83]. Infected neurons produce IFN-α, IFN-β, IL-1β, CXCL1, and CXCL10 [49,84,85,86]. Furthermore, neurons exert deregulated expression of miRNAs, e.g., up-regulated miRNA-146a [87].