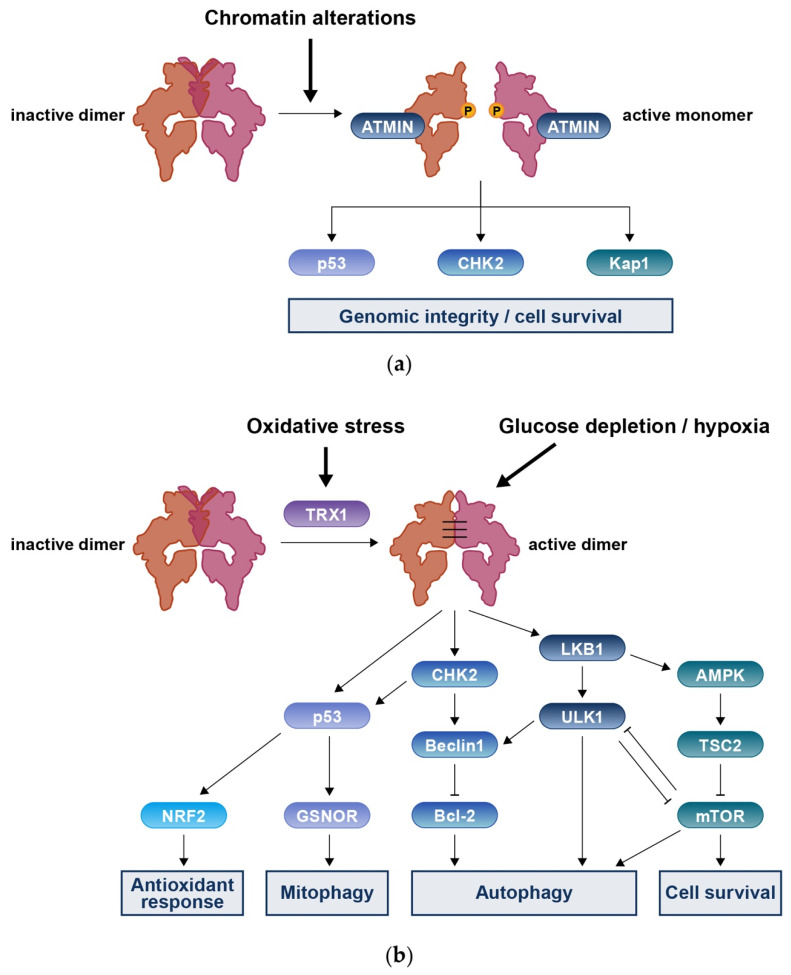
Figure 3.
(a) Chromatin alterations trigger ATM activation through interaction with ATMIN. ATMIN competes with NBS1 in binding to ATM. Activated ATM phosphorylates and activates p53, CHK2, and Kap1 to promote genomic integrity and cell survival. (b) Oxidative stress can also trigger ATM activation through forming intermolecular disulfide bonds in the manner depending on TRX1. Glucose depletion or hypoxia also activate ATM. To reduce oxidative stress or other cellular stress, ATM then activates transcription of genes involved in the antioxidant response. ATM also promotes autophagy and mitophagy to maintain ROS homeostasis while suppressing mTORC1.