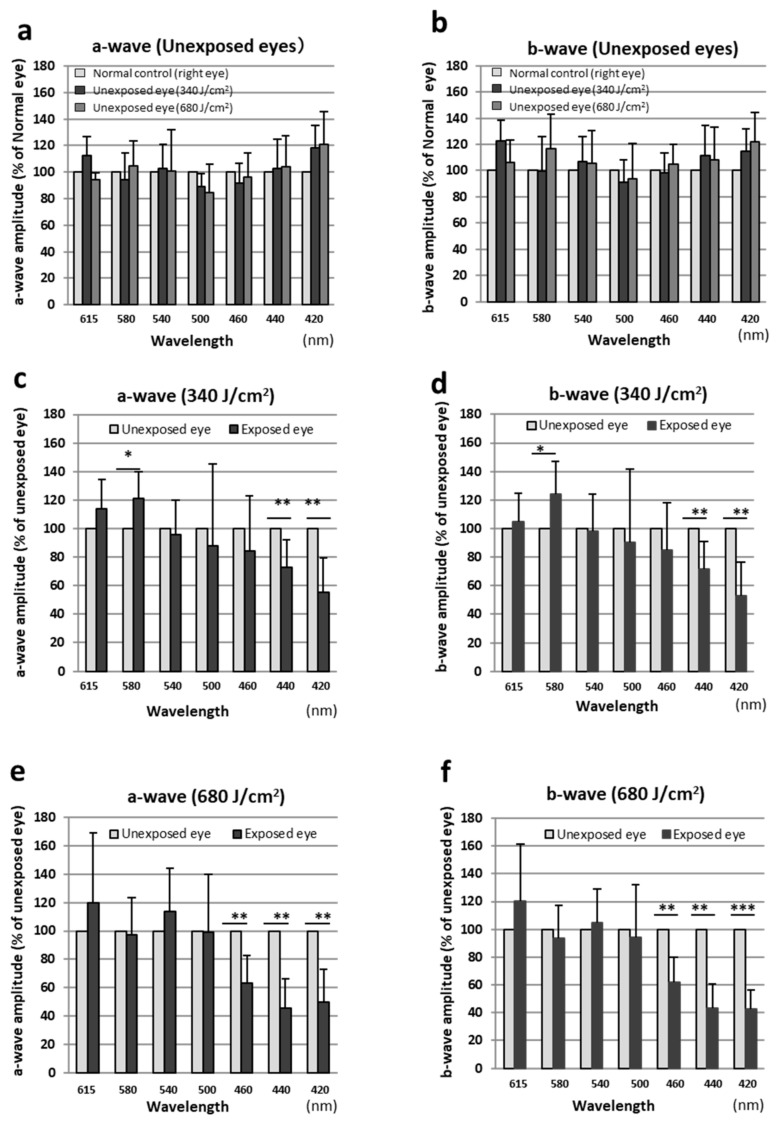
Figure 1.
Measurement of retinal function by electroretinography. Data were expressed as mean ± SD. (a) The a-wave amplitude (% of the amplitude in normal control right eyes) for unexposed right eyes. (b) The b-wave amplitude (% of the amplitude in normal control right eyes) for unexposed right eyes. (c) The a-wave amplitude (% of the amplitude in unexposed right eyes) for eyes exposed to 340 J/cm2 light. (d) The b-wave amplitude (% of the amplitude in unexposed right eyes) for eyes exposed to 340 J/cm2 light. (e) The a-wave amplitude (% of the amplitude in unexposed right eyes) for eyes exposed to 680 J/cm2 light. (f) The b-wave amplitude (% of the amplitude in the unexposed right eyes) for eyes exposed to 680 J/cm2 light. Both eyes were compared using the paired t-test, and between-group comparisons were performed using the unpaired t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. n = 6 in each group.