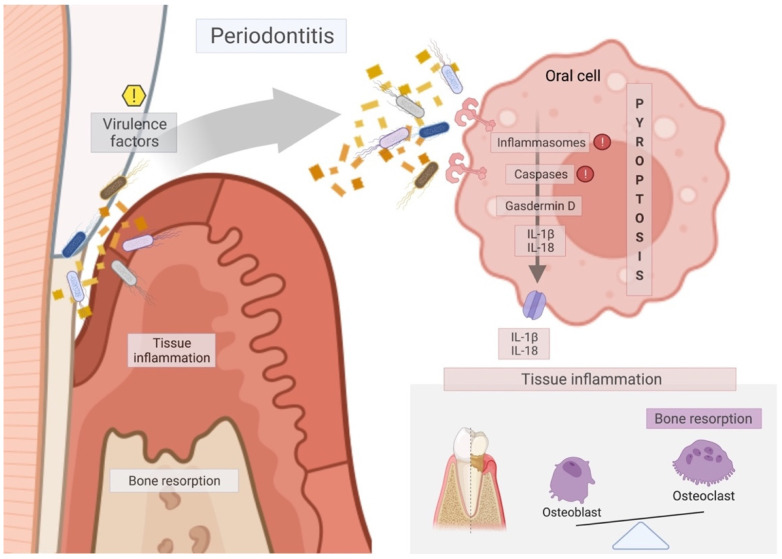
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the mechanism of pyroptosis pathway on periodontal tissues to the promotion of periodontitis. Virulence factors activate the inflammasome/caspase downstream to the cleavage of Gasdermin D, which is responsible for membrane pore formation and, thus, the release of interleukins IL-1β and IL-18 to the extracellular environment. Those interleukins lead to tissue inflammation and disruption of the balance between bone formation by the osteoblasts and bone resorption by the osteoclasts, thus aggravating the process of periodontitis through soft tissue inflammation (swelling, bleeding) and marginal bone loss. Red exclamation marks mean the main targets for pyroptosis-specific inhibitors, such as MCC950, Ac-YVAD-CHO, Z-LEVD-FMK, and VX765. Yellow exclamation mark indicates the main target for therapeutic approaches that should act on the virulence factors responsible for triggering pyroptosis on periodontal tissues.