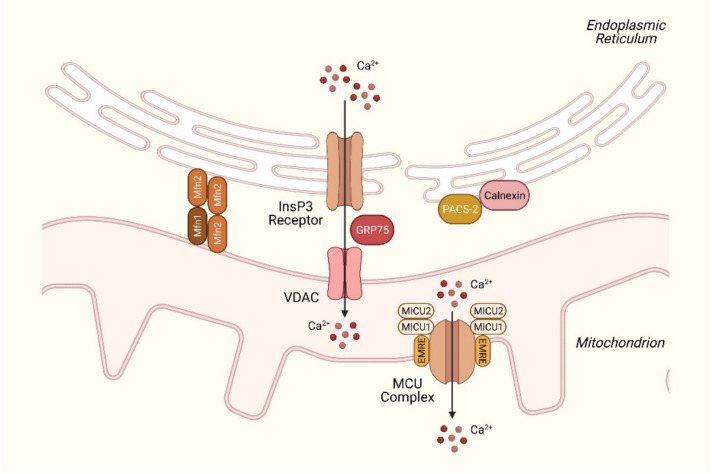
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of Ca2+ flux at the ER–mitochondria contact sites. The ER and mitochondria are functionally coupled through physical interactions at contact sites (also known as MAMs), allowing Ca2+ transport from the ER to mitochondria through the InsP3 receptor and VDAC. The two ion channels are connected by the chaperone GRP75. The MAM structure is stabilized by tethering proteins Mfn1/2 and interactions between calnexin and PACS-2. Ca2+ enters the mitochondrial matrix via the MCU complex at the inner mitochondrial membrane. MCU-binding proteins MICU1/2 control the opening of the channel, while EMRE assists the MCU–MICU interaction and regulates the complex activity. Abbreviations: InsP3, inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate; Mfn1/2, mitofusin 1/2; VDAC, voltage-dependent anion channel; MCU, mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter; MICU1/2, mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake 1/2; EMRE, essential MCU regulator.