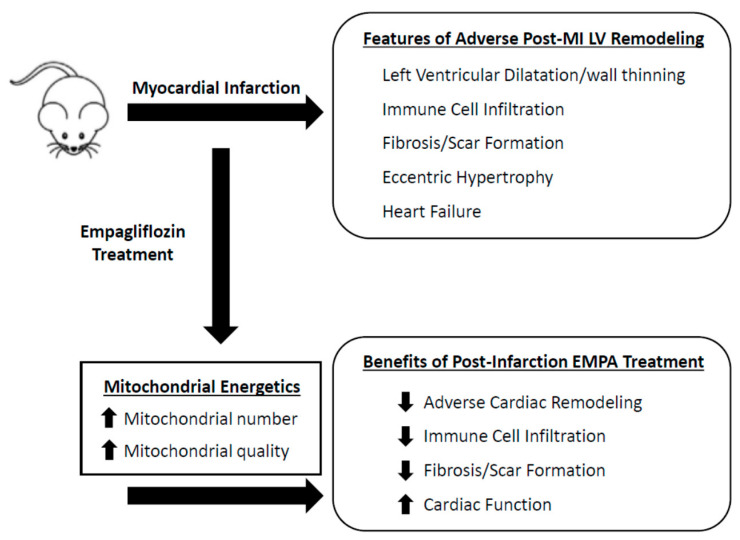
Figure 6.
Empagliflozin attenuates infarct-induced adverse cardiac remodeling. Post-MI administration of empagliflozin leads to improved mitochondrial energetics by increasing mitochondrial biogenesis and enhancing the quality of the mitochondrial population in cardiac cells. This is associated with decreasing immune cell infiltration to the border zone, decreasing fibrosis and scar formation and ultimately attenuating adverse remodeling of the heart and delaying the onset of heart failure.