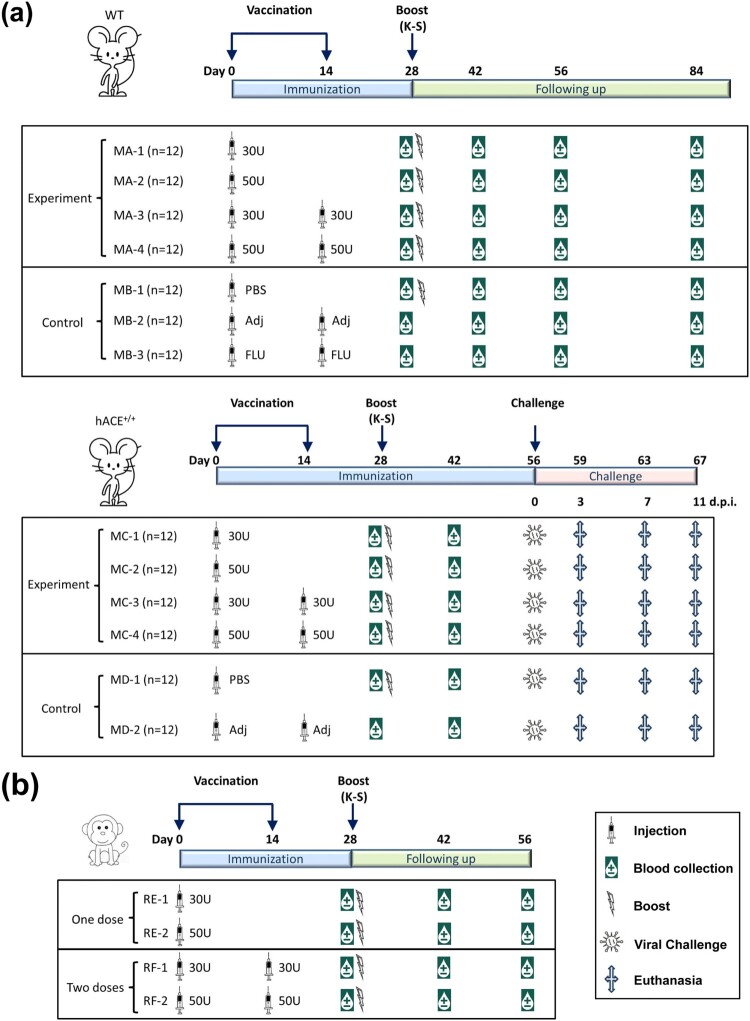
Figure 1.
. Design of animal immunization schedule and viral challenge. (a) Mouse immunity and challenge experiment. This experiment included hACE2 transgenic mice (MC and MD groups) and WT mice (MA and MB groups). The mice received intradermal injections (ID; syringe signs) with different doses (30 or 50 U) of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, PBS, adjuvant (Adj), and inactivated influenza vaccine (FLU) through different procedures (one or two injections at an interval of 14 days). Some mice were boosted (thunder-like signs) with the K-S antigen (10 μg/dose). Blood samples (water drop-like signs) were obtained on days 28 and 42 after the first immunization in hACE2 transgenic mice (MCs and MBs), and on days 28, 42, 56, and 84 after the first immunization in WT mice (MAs and MBs) for antibody assays. Viral challenge (virus-like signs) was performed on day 56 after the first immunization in hACE2 transgenic mice (MAs and MBs). At days 3, 7, and 11 after the viral challenge, three mice from each group were euthanized (cross signs) for viral load measurement and pathological observation. MBs were the control groups for MAs, and MDs were the control groups for MCs (n = 12 per subgroup). (b) Rhesus macaque immunity experiment. The macaques received intradermal injections (ID; syringe signs) of different doses (30 or 50 U) of inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine through different procedures (one or two injections at an interval of 14 days). The macaques were boosted (thunder-like signs) with the K-S antigen (10 μg/dose) on day 28 after the first immunization. Blood samples (water drop-like signs) were obtained on days 28, 42, and 56 after the first immunization for antibody assays (n = 4 per subgroup).