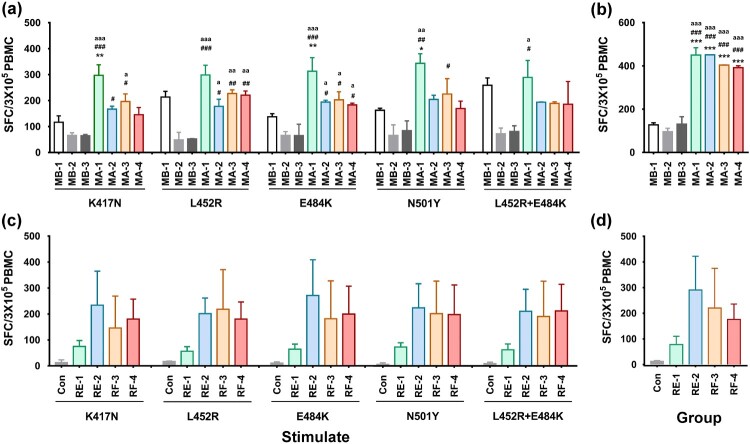
Figure 5.
Development of a specific T cell response against different antigens from variants in individuals immunized with the heterologous vaccine administered via the ID route. (a) Specific T cell responses against RBD protein with five variants (four single-point mutation RBD proteins and a single two-point mutation RBD protein) were induced in immunized mice of the MA group compared to the MB group. (b) Specific T cell responses against N proteins were induced in immunized mice of the MA groups compared to MB groups. (c) Specific T cell responses against RBD proteins with five variants (four single-point mutation RBD proteins and a single two-point mutation RBD protein) were induced in immunized macaques from the RE and RF groups. (d) Specific T cell responses against N proteins were induced in immunized macaques in the RE and RF groups. The blood samples were obtained on day 28 after boosting with the K-S antigen. In the monkey experiment, blood samples were obtained from three untreated, healthy macaques included in the control group (Con). Statistical significance was assessed by two-way ANOVA. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01;***; p < 0.001 versus MB-1 group; #, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01; ###, p < 0.001 versus MB-2 group; a, p < 0.05; aa, p < 0.01; aaa, p < 0.001 versus MB-3 group in WT mice (n = 12 per subgroup). There was no significant difference in monkeys between different subgroups (n = 4 per subgroup and n = 3 in control).