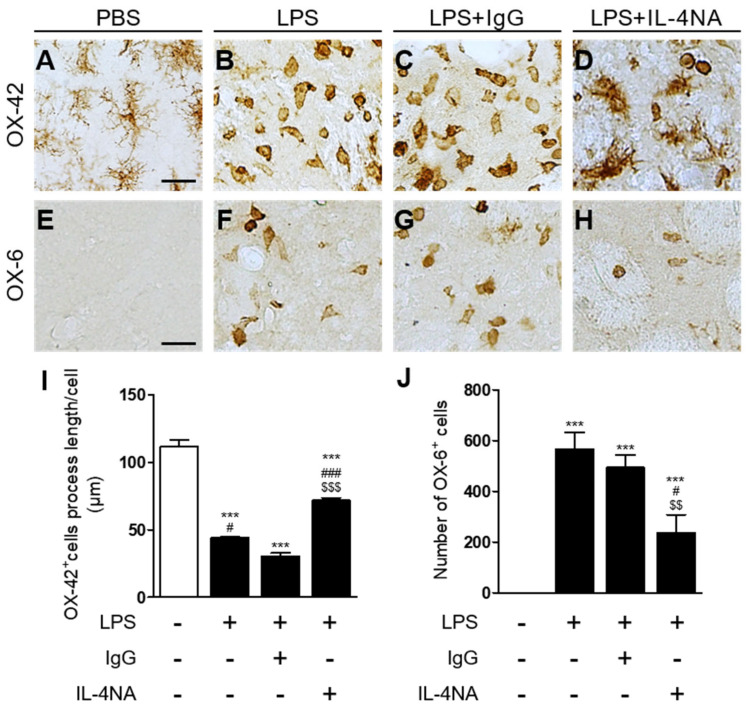
Figure 4.
IL-4 contributes to microglial activation in the LPS-injected striatum in vivo. Animals intrastriatally received a unilateral injection of PBS (A,E) as a control, LPS (B,F), LPS+non-specific IgG (1 µg/µL; (C,G)), and LPS+IL-4NA (1 µg/µL; (D,H)). At 3 days after injection, animals were transcardially perfused and brain tissues were processed for OX-42 immunostaining (A–D) or OX-6 (E–H) immunostaining at 3 days post LPS. (I) Quantification of OX-42 process length. *** p < 0.001, significantly different from PBS (control). ### p < 0.001, significantly different from LPS. Mean ± SEM; n of animals = 4 to 5 in each group. ANOVA and Bonferroni analysis. (J) Number of OX-6+ cells in the LPS-injected striatum (total area = 4.6 × 105 μm2). *** p < 0.001 significantly different from PBS (control), # p < 0.01 significantly different from LPS mean ± SEM; n of animals = 4 to 5 in each group. ANOVA and Bonferroni analysis. # p < 0.05, significantly different from LPS. ### p < 0.001, significantly different from LPS+IgG. $$ p < 0.01, significantly different from LPS. $$$ p < 0.001, significantly different from LPS.