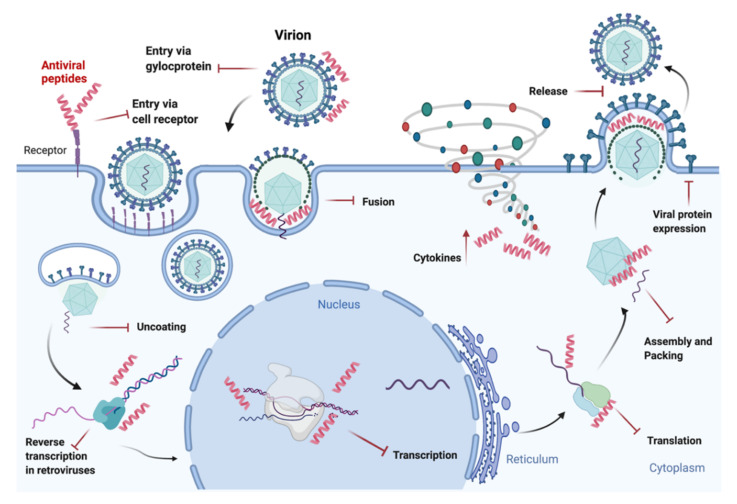
Figure 2.
AVPs targets in viral life cycle. Depending on the type of virus and on the mode of action of the peptides, AVPs can block viral entry by binding with specific cellular receptors or interaction with viral glycoproteins, which are involved in both entry and fusion process. They may also hinder the fusion via physicochemical interaction with hydrophobic membrane–protein interfaces. AVPs can act intracellularly as well by direct influence of viral nucleic acid synthesis or blocking viral protein expression. Others modulate the antiviral immune system of the host cell by up-regulating expression of interferons and cytokines.