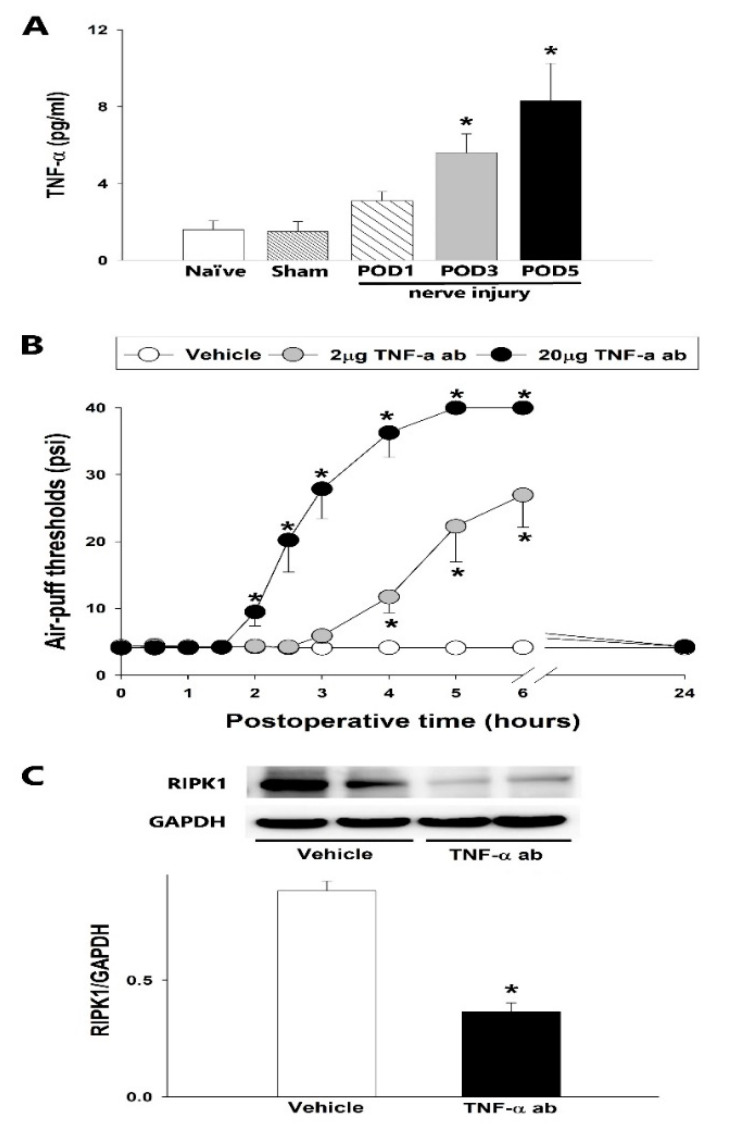
Figure 4.
Effects of TNF-α antibody (ab) treatment of the trigeminal subnucleus caudalis upon mechanical allodynia and RIPK1 expression. (A) Time-course analysis of the changes in the TNF-α concentration after an inferior alveolar nerve injury produced by a malpositioned dental implant. ELISA analysis revealed significant increases in TNF-α concentration (one-way ANOVA with Holm–Sidak post hoc tests, n = 8) in the sham vs. inferior alveolar nerve injury POD 1, 3, and 5. (B) The intracisternal administration of TNF-α antibodies increased the air-puff thresholds compared with the vehicle-treated group (repeated measure ANOVA with Holm–Sidak post hoc tests, n = 7). Vehicle vs. 2 or 20 µg TNF-α-ab-treated group. (C) Western blot analysis revealed that RIPK1 expression was downregulated at 6 h after an intracisternal treatment with 20 µg TNF-α antibody on POD 3 compared with the vehicle group (Student’s t-test, n = 8). Vehicle vs. TNF-α-antibody-treated group. GAPDH was used as a loading control. All mean ± SEM, * p < 0.05.