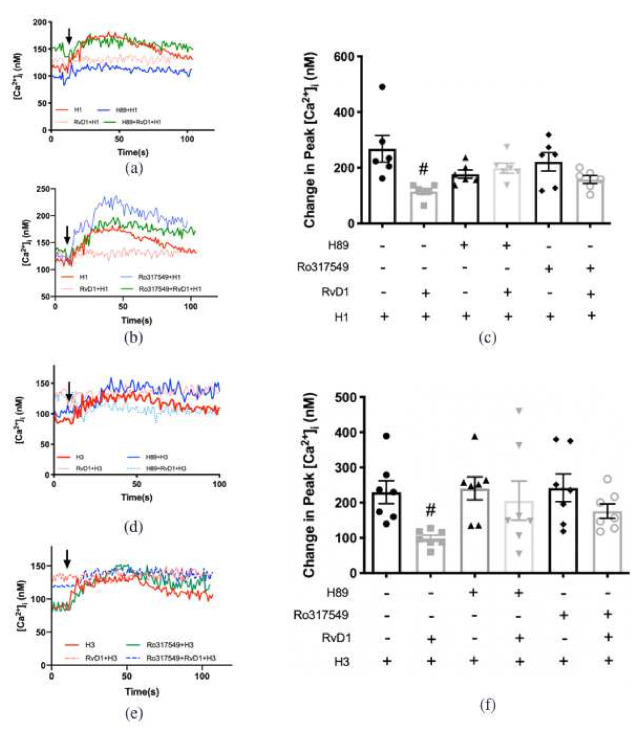
Figure 10.
RvD1 uses both PKA and PKC to counter-regulate the increase in [Ca2+]i induced by H1 and H3 specific agonists. H1 agonist (histamine dimaleate,10−6 M) (a,b) and H3 agonist ((R)-(-)-α-methylhistamine, 10−5 M) (c,d), were added alone (solid red line in a,c; first bar in b,d). RvD1 (10−8 M) was added followed by H1 (a,b) or H3 (c,d) agonist 30 min later (solid pink line in a,c; second bar in b,d). PKA inhibitor H89 (10−5 M) was given 30 min prior to addition of H1 (a,b) or H3 (c,d) agonist (blue line in a,c; third bar in b,d). PKA inhibitor H89 (10−5 M) was given 15 min prior to RvD1 (10−8 M) treatment followed 30 min later by H1 (a,b) or H3 (c,d) agonist (dashed blue line in a,c; fourth bar in b,d). PKC inhibitor Ro317549 (10−7 M) was given 30 min prior to addition of H1 (a,b) or H3 (c,d) agonists (green line in a,c; fifth bar in b,d). PKC inhibitor Ro317549 (10−7 M) was given 15 min prior to RvD1 (10−8 M) treatment followed 30 min later by H1 (a–c) or H3 (d–f) agonist (dashed blue line in a,b; sixth bar in b,d). The average [Ca2+]i level over time was shown in (a,b,d,e); change in peak [Ca2+]i was calculated and shown in (c,f). Data are mean ± SEM from 6 rats for (a–c), 7 rats for (d–f). # Indicates a significant difference from stimulus alone. Arrow indicates addition of histamine receptor subtype agonist.