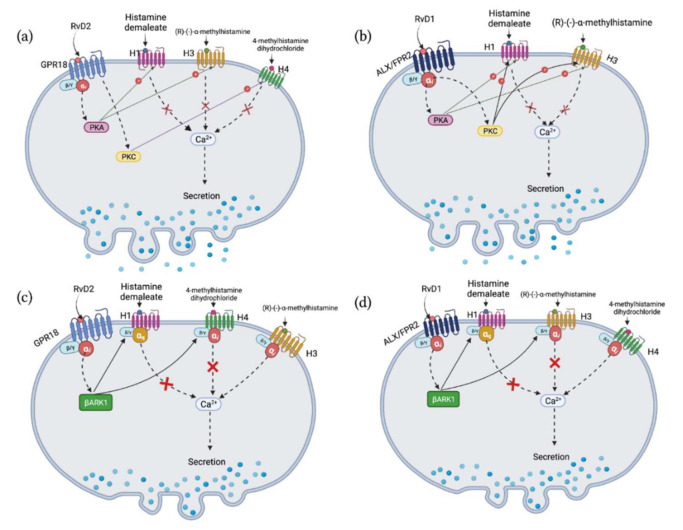
Figure 11.
Summary of protein kinases used by RvD2 and RvD1 to counter-regulate increase on [Ca2+]i induced by histamine receptor subtype agonists. RvD2 counter-regulates histamine-induced [Ca2+]i increase by interaction with H1, H3, and H4 receptors (a,c). RvD2 uses PKA to counter-regulate [Ca2+]i increase induced by H1 and H3 specific agonists, but uses PKC to regulate the H4 specific agonist (a). RvD2 Uses β-ARK1 to counter-regulate [Ca2+]i increase induced by H1 and H4 specific agonists, but not H3 specific agonists (c). RvD1 counter-regulates histamine-induced increase in [Ca2+]i by interaction with H1 and H3 (b,d). RvD1 uses PKA and PKC (b) and β-ARK1 (d) to counter-regulate increase in [Ca2+]i induced by both H1 and H3 specific agonists. Solid lines with arrowheads indicate direct interaction; dash lines with arrowheads indicate indirect interaction; letter P in a circle indicates phosphorylation; and red crosses on the lines indicate this pathway is inhibited. Abbreviations: H1–H4, histamine receptor subtype 1–4; histamine dimaleate, H1 agonist; (R)-(-)-α-methylhistamine, H3 agonist; 4-methylhistamine dihydrochloride, H4 agonist; RvD, resolvin D; PKA, protein kinase A; PKC, protein kinase C; β-ARK1, β adrenergic receptor kinase 1; GPR18, G protein coupled receptor 18; ALX/FPR2, G-protein coupled formyl peptide receptor 2.