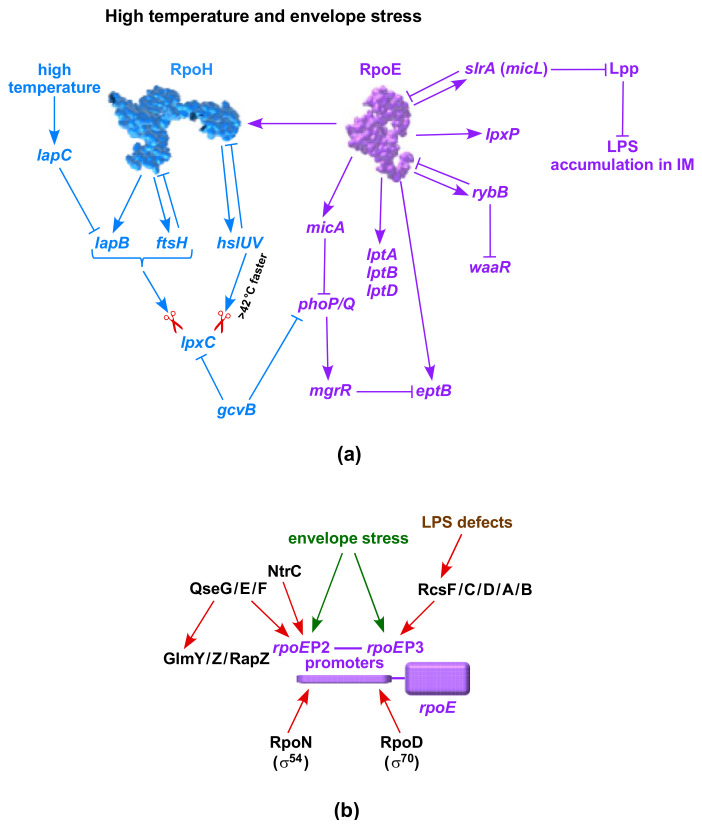
Figure 5.
Alternative sigma factors RpoH and RpoE induced at high temperatures and envelope stress, respectively, control several essential processes in LPS biosynthesis. (a) The expression of LapC, LapB, FtsH and HslVU regulating LpxC turnover are induced at high temperatures. Genes encoding LapB, FtsH and HslVU are members of the RpoH regulon. RpoE is required for the transcription of several genes involved in LPS biosynthesis and also activates the transcription of the rpoH gene at high temperatures. sRNAs MicA, RybB and SlrA constitute the non-coding arm of the RpoE regulon. MicA and RybB are involved in the regulation of LPS modifications. The overproduction of SlrA represses the Lpp synthesis, thereby relieving the accumulation of toxic buildup of LPS in the IM in the absence of LapB and thus repressing the hyperinduction of RpoE in such backgrounds. (b) Severe envelope stress due to LPS defects induces the transcription of the rpoE gene via the induction of rpoEP2 and P3 promoters, particularly rpoEP3, which requires Rcs system activation.