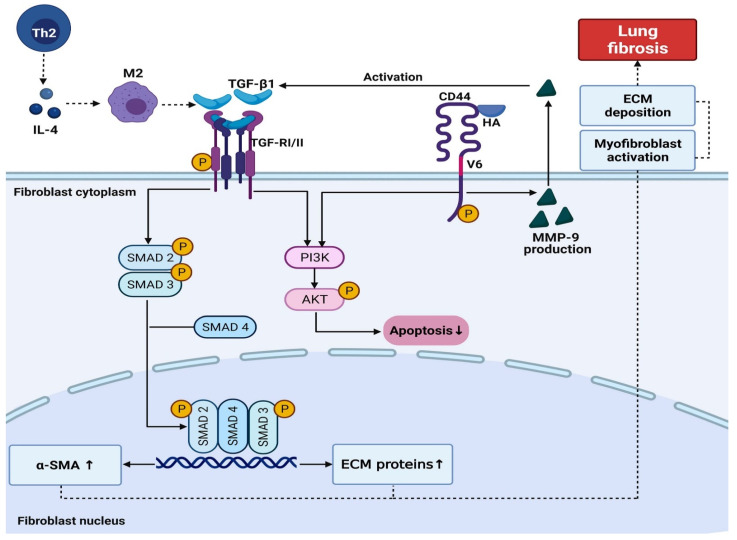
Figure 5.
IL-4 mediates the functions of Th2 cells. IL-4 induces the alternative activation of M2 macrophages, which, in turn, secrete TGF-β1, stimulating fibroblast proliferation. The TGF-β type I and type II receptors (TGFRI and II) activate several intracellular signaling cascades, including the canonical SMAD2/3-4 and the noncanonical PI3K/AKT pathways. Once active, TGFRI triggers the complex SMAD2/3-4 that binds profibrotic genes and induces fibrogenic proteins expression such as α-SMA and Collagen I (mature), resulting in induction myofibroblast activation and ECM deposition. The PI3K/AKT pathway, on the other hand, increases the resistance of fibroblasts and the proliferation of myofibroblasts. Furthermore, once the CD44v6/HA complex is formed, the PI3K/AKT pathway leads to fibroblasts’ resistance to apoptosis. This CD44v6/HA interaction increases the production of MMP-9, which leads to the activation of TGF-β1.