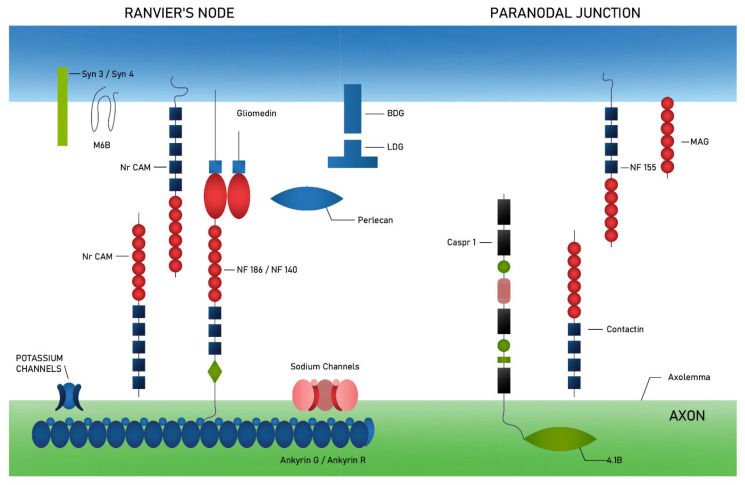
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the proteins that make up the Ranvier’s node and paranodal junction. On the axonal side, the Ranvier’s node consist of sodium channels (NaCh) and diverse (mechanically and voltage-gated) potassium channels (K channels), which are associated with ankyrin G and ankyrin R proteins—linking membrane proteins to the spectrin-actin complex cytoskeleton—and at the same time with neurofascin 186 (NF186) or neurofascin 140 (NF 140). Adhesion complex in paranodal region composes of contactin and contactin associated protein-1 (Caspr 1), which bind to protein 4.1B. Schwann cells express in Ranvier’s node several transmembrane proteins such as protein belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily (NrCAM), dystroglycan (αDG and βDG), syndecan 3 and 4 (Syn3 and Syn4) and protein M6B. In paranodal junction, myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) and neurofascin 155 (NF 155) are expressed [26].