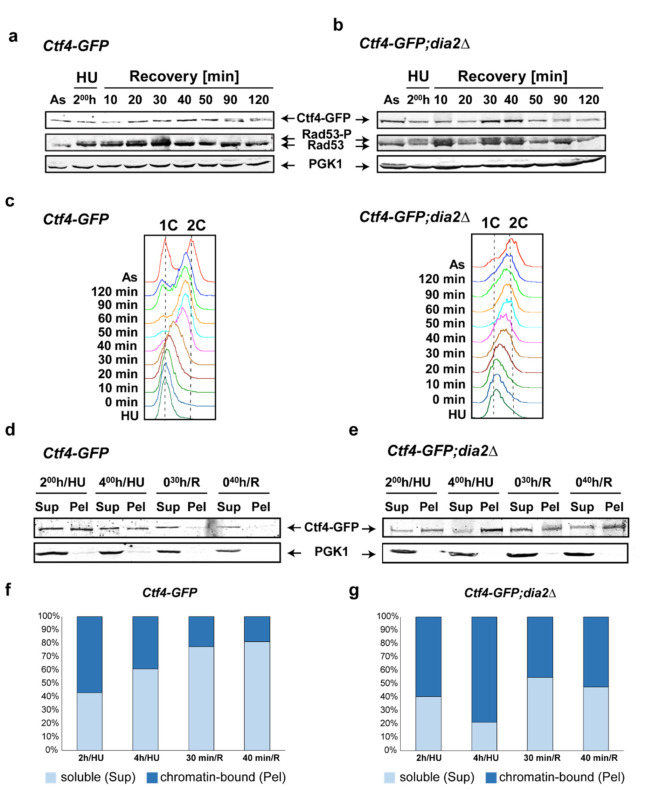
Figure 3.
Western blot analysis of Ctf4 profile. (a,b) Immuno-detection of Ctf4-GFP, Rad53, and PGK1 (loading control) was carried out from total protein extracts obtained at the indicated time points from both Ctf4-GFP and Ctf4-GFP;dia2Δ strains. Rad53-P and Rad53 indicate the phosphorylated and unphosphorylated forms of Rad53 protein, respectively. The presence of Rad53-P indicates the activation of the S-phase checkpoint. (c) Flow-cytometry analysis at the indicated time points for both strains. (d,e). Chromatin fractionation assay of Ctf4-GFP and Ctf4-GFP;dia2Δ strains. Samples from the indicated time points were separated into chromatin-bound (Pel) and unbound/soluble (Sup) fractions. The cytoplasmic protein PGK1 was used as an internal loading control. (f,g) Relative amounts of chromatin-bound (Pel) and soluble (Sup) Ctf4-GFP from the two strains. For each time point, the ratio of the Sup to the Pel is represented; As—asynchronous cell culture; HU—hydroxyurea-arrested cells; R—recovery time point, Sup—Supernatant; Pel—Pellet.