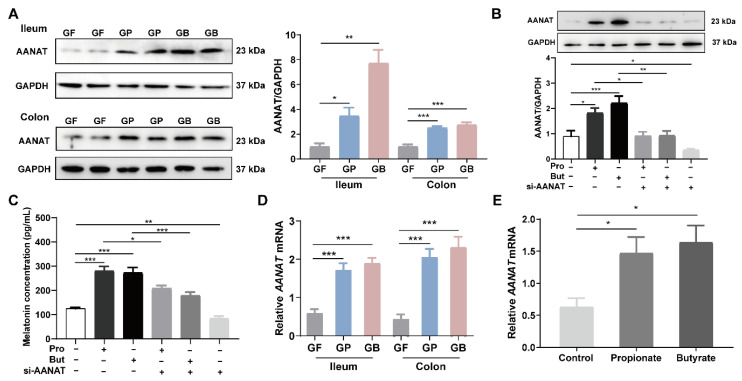
Figure 4.
Propionate and butyrate increased intestinal AANAT level in rats. (A) Representative images (left) and quantification of intestinal AANAT level (right) detected using Western blotting after administration of sodium propionate or sodium butyrate to germfree rats. Analysis was performed using Brown–Forsythe and Welch ANOVA test with Tamhane’s T2 post-hoc test (n = 6). (B) Representative images (above) and quantification of AANAT level (below) in BON-1 cells after propionate/butyrate (10 mM) treatment for 24 h with or without Aanat siRNA treatment for 32 h. Results were obtained using Western blotting and analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. n = 6. (C) Melatonin concentration in BON-1 cell supernatant after propionate/butyrate (10 mM) treatment for 24 h with or without Aanat siRNA treatment for 32 h. Results were detected using ELISA and analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test (n = 6). (D) Intestinal Aanat mRNA expression normalized to β-actin expression after administration of sodium propionate or sodium butyrate to germfree rats. Results were obtained using qPCR and analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test (n = 6). (E) Aanat mRNA expression normalized to β-actin expression in BON-1 cells after treatment with propionate/butyrate (10 mM) for 24 h. Analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test (n = 6). GF, germfree rats receiving PBS gavage; GP, germfree rats receiving propionate gavage; GB, germfree rats receiving butyrate gavage. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.