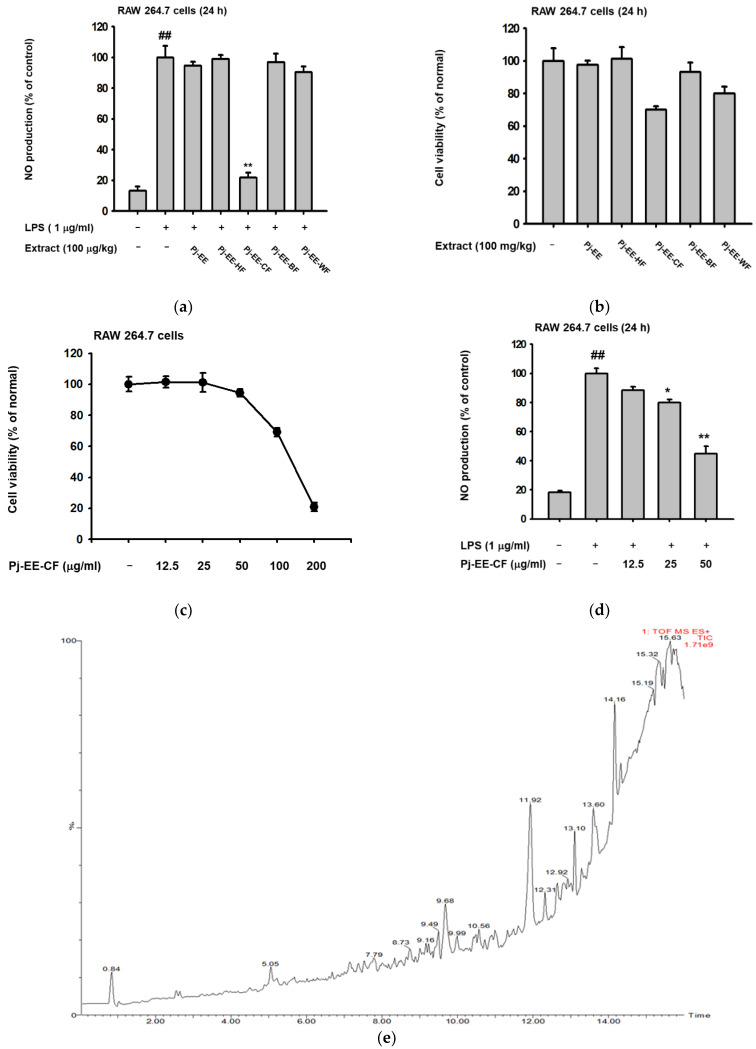
Figure 1.
Effect of Pj-EE and its solvent fractions on the production of NO, cell viability profile, and phytochemical constituents of Pj-EE-CF. (a,d) Supernatant NO levels on LPS (1 μg/mL)-induced RAW264.7 cells pretreated with 100 μg/mL of Pj-EE, Pj-EE-HF, Pj-EE-CF, Pj-EE-BF, or Pj-EE-WF (a) and with the indicated concentrations of PJ-EE-CF (d) were analyzed using the Griess assay. (b,c) Cell viability of RAW264.7 cells upon treatment with Pj-EE, Pj-EE-HF, Pj-EE-CF, Pj-EE-BF, or Pj-EE-WF (b) and PJ-EE-CF (c) at the same concentration on NO assay were analyzed using an MTT assay. (e) The phytochemical screening performed on Pj-EE-CF using LC/MS-MS chromatogram. Results (a–d) are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. ## p < 0.01 compared to normal group (no treatment), and * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared to control group (LPS alone) by one-way ANOVA.