Fig. 3.
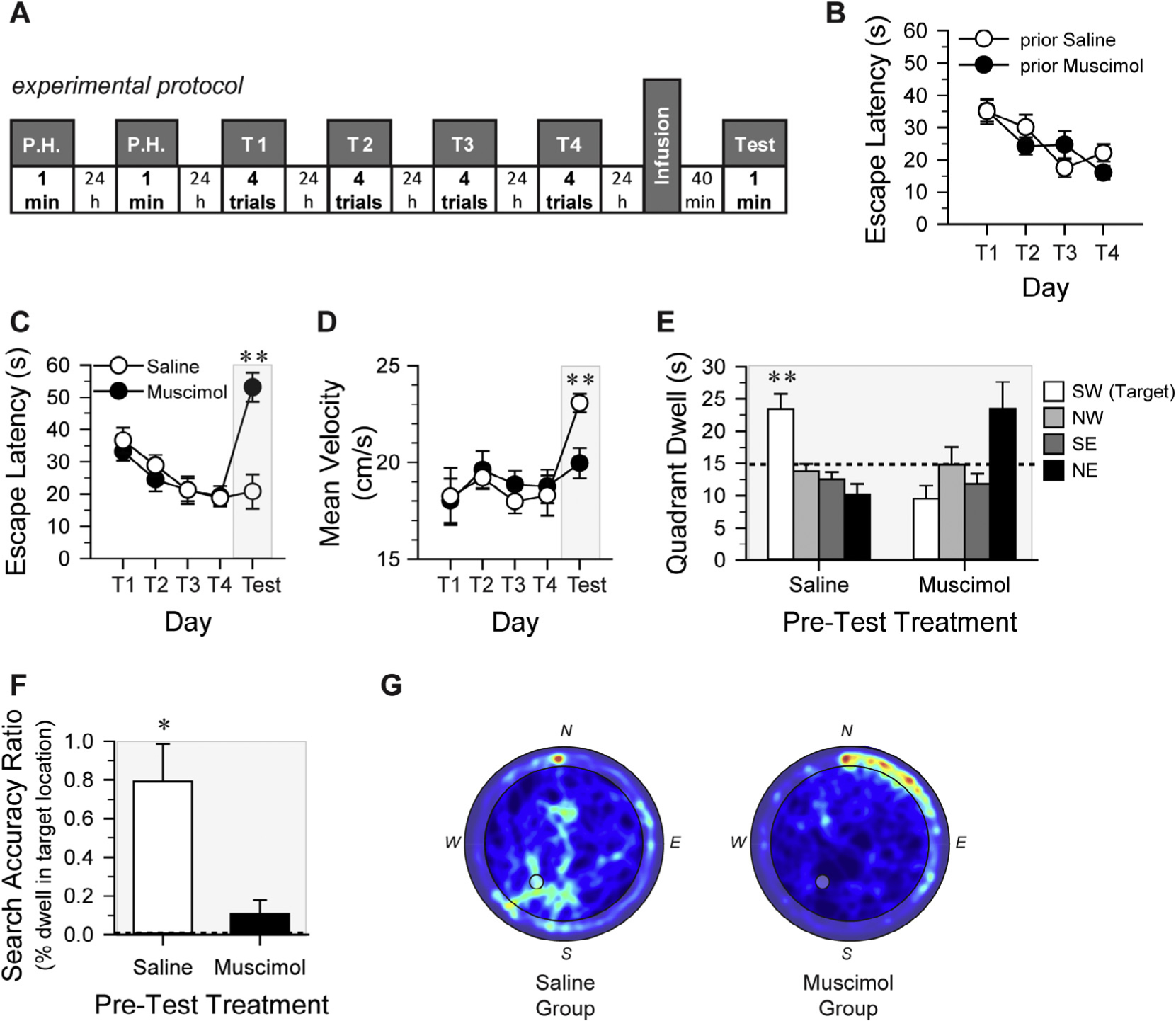
Pre-test intra-CA1 muscimol impairs retrieval of long-term spatial memory and memory for task performance. A. Schematic of the experimental protocol used for the MWM task. P.H.: Pool Habituation (exposure to the pool without extra-maze visual cues, platform in center of pool); T1-T4: Training sessions comprising 4 trials/day (spatial training with extra-maze visual cues and platform in SW quadrant); Test: platform-less probe test of spatial memory retention. Mice received intra-CA1 saline or muscimol 10–11 days prior to the onset of MWM training (see Fig. 2D). B. Escape latency across the four training sessions plotted according to the previous intra-CA1 treatment (prior Saline, prior Muscimol). Prior intra-CA1 treatment did not affect spatial training in the MWM, indicating that the effects of muscimol on CA1 were temporary. Treatment assignments for pre-MWM probe test microinfusions were reversed from that of pre-NOP test session. Escape latency (C) and mean velocity (D) plotted according to MWM pre-probe test treatment. There was no effect of future treatment on either dependent measure across training trial blocks. However, pre-test muscimol-treated mice took a significantly longer latency to reach the platform location than did the pre-test saline-treated mice (P < 0.001), indicating impaired retrieval of spatial memory. The mean velocity of pre-test saline-treated mice was significantly greater than that of the pre-test muscimol-treated mice. E. Mice that received pre-probe test intra-CA1 saline spent significantly more time in the target SW quadrant than in any other quadrant, and more time in the target quadrant than did the muscimol-treated mice. Although pre-test intra-CA1 muscimol-treated mice spent more time in the NE quadrant, they failed to exhibit a statistically significant preference for any quadrant. Dashed line indicates chance performance: 15 s dwell in a given quadrant. F. Specific search accuracy was calculated by finding the percentage of time during the 60-s probe test that each mouse spent in the exact location of the pool where the platform had been during training. Pre-test saline-treated mice exhibited a significantly greater search accuracy ratio than would be expected by chance (see dashed line at 0.005696; P = 0.002); however, muscimol-treated mice did not perform better than chance. G. Composite map of all swim paths during the probe test for each pre-test treatment condition. Plots present quadrant dwell as a “heat map” representing mean dwell times according to a color code with darker, cooler colors indicating low dwell times and warmer colors indicating high dwell times. The pre-test saline-treated mice appropriately concentrated their search in the SW quadrant, while the pre-test muscimol-treated mice failed to concentrate their search in the SW quadrant and instead demonstrate predominant thigmotaxis. The gray circle in center of the SW quadrant of each composite image indicates the location where the platform had been submerged during training. All error bars indicate ± S.E.M. *, P < 0.01; **, P ≤ 0.001. The gray shaded boxes in plots C–F indicate behavioral testing that occurred under the influence of the respective intra-CA1 treatment.
