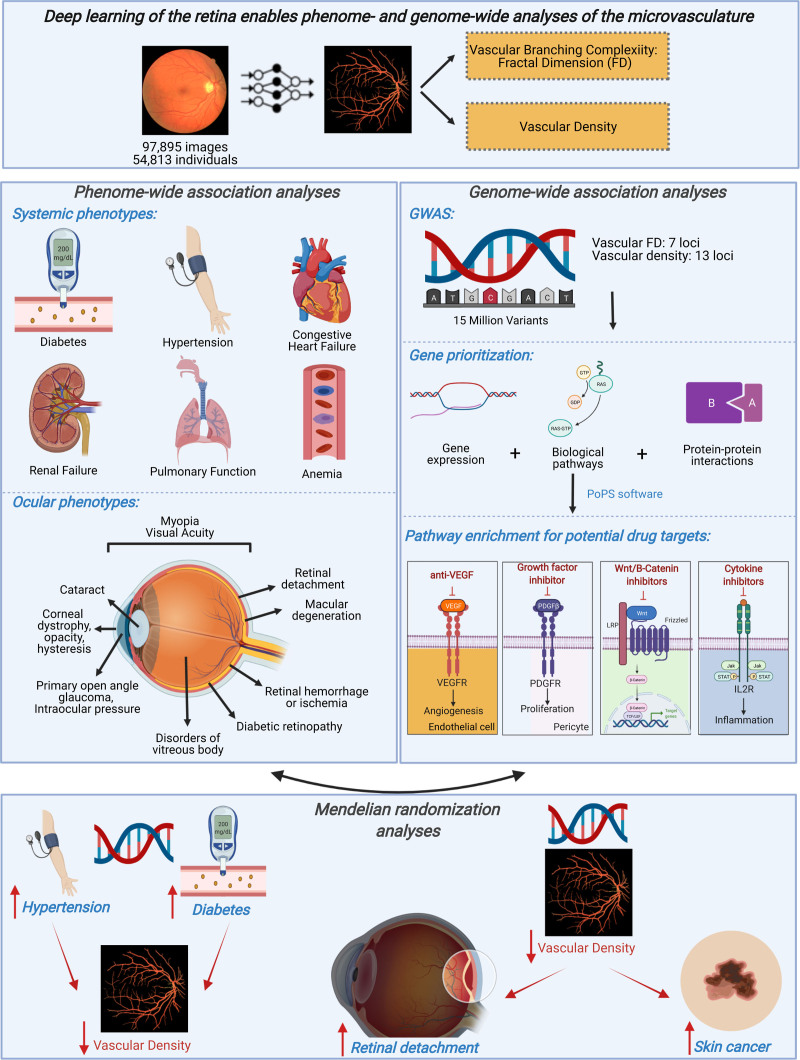
Figure 8.
Summary of key findings. Here, we successfully implemented deep learning toward image quality control and vessel segmentation to extract 2 features of the retina: vascular density and fractal dimension (FD). Through phenome-wide analyses, we identified significant associations between low vascular density and FD and higher risk of multiple systemic and ocular phenotypes, including ocular conditions influencing both the anterior and posterior segments. Genome-wide association analyses of these microvascular indices discovered multiple loci enriched among pathways related to vascular biology, inflammation, and neovascularization in cancer and may hypothesize potential drug targets for risk modification. Mendelian randomization analyses identified that higher genetic risk for hypertension and type 2 diabetes is associated with lower microvascular density and that higher genetic risk for lower microvascular density is associated with retinal detachment (independently of myopia) and with skin cancer (independently of genetic ancestry principal components, self-reported skin color, and self-reported sun exposure and sun sensitivity). More broadly, our results illustrate the potential for using deep learning on retinal imaging to understand the microvasculature, with wide applications across diseases. This image was made with Biorender. GWAS indicates genome-wide association study.